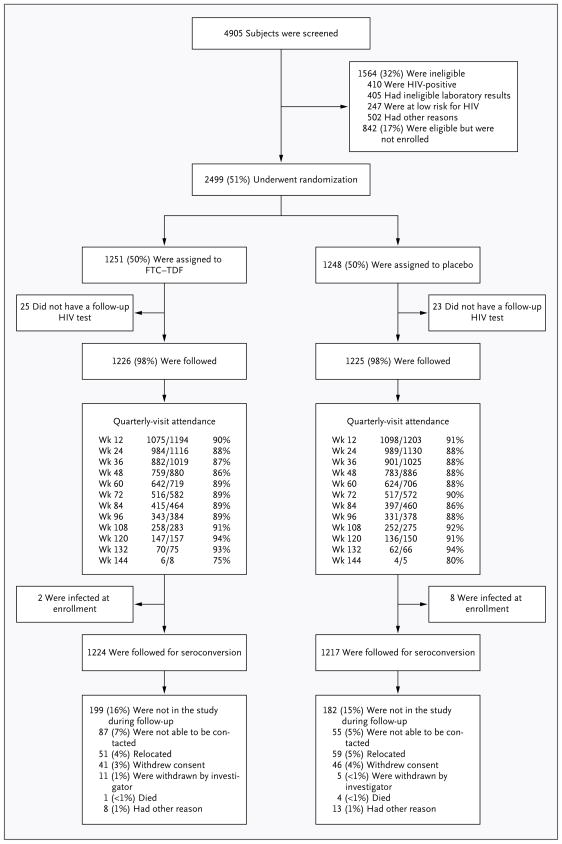
Figure 1. Enrollment and Outcomes.
The most common laboratory abnormalities that led to exclusion were elevations in hepatic aminotransferase levels, hyperbilirubinemia, and renal insufficiency. A total of 18 enrollees (0.7%) did not meet all eligibility criteria, including 2 subjects with preexisting diabetes mellitus, who were instructed to stop taking a study drug when the history was discovered. All enrolled subjects, including those who were subsequently found to be ineligible, were followed for HIV infection and safety. Quarterly-visit attendance is shown. Visits were considered to have been completed if they occurred before the subsequent visit window, with completion rates of 75 to 94% for all visits. The completion rate was more than 86% for all visits before week 132. Visits occurred within the protocol-defined window of ±5 days in 62 to 86% of visits.