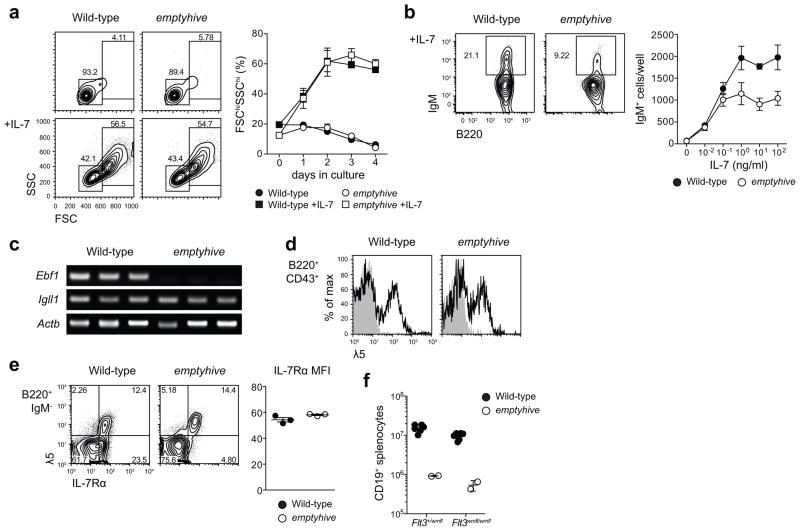
Figure 4.
Sensitivity to IL-7 and a failure to sustain expression of Ebf1. (a) B220+ surface IgM−bone marrow cells were sorted by flow cytometry and cultured ex vivo in the presence or absence of 100 ng/ml IL-7, and percentages of 7-AAD− lymphoblasts (FSChiSSChi) were measured at daily intervals. Symbols and error bars represent the mean and standard error of three mice per genotype. (b) B220+ surface IgM− bone marrow cells sorted from wild-type (CD45.1) or emptyhive (CD45.2) mice were cocultured in the presence of various concentrations of IL-7. Following four days of culture, frequencies and numbers of 7-AAD−surface IgM+ cells were measured. Symbols and error bars represent the mean and standard error of three mice per genotype. (c) RT-PCR PCR of cDNA from pre-pro-B cells (7-AAD−B220+IgM/IgD−CD19−NK1.1−Ly6C−). Each lane represents an individual mouse. (d) λ5 (CD179b) expression on the surface of B220+CD43+ bone marrow lymphocytes. Shaded histograms represent rat IgG2a isotype control, while solid histograms show λ5 staining. (e) IL-7Rα (CD127) expression on the surface of B220+IgM− bone marrow lymphocytes (dot plots, left), or B220+IgM−λ5+ (mean fluorescence intensity, right). (f) Splenic B cell numbers in emptyhive mice with combined mutation of Flt3. All data are representative of two independent experiments, each with three mice per genotype.