Figure 1. Physiologic consequences of JNK signaling in Drosophila.
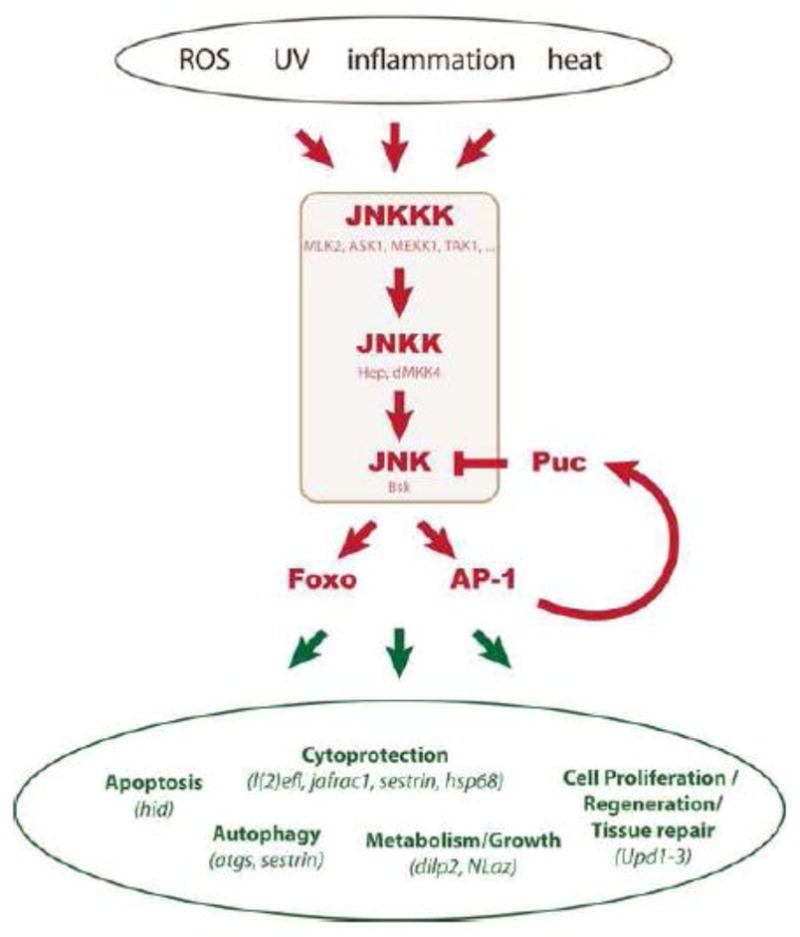
The Drosophila JNK signaling pathways consists of a single JNK (Basket), two JNKKs (Hemipterous and dMKK4) and a number of JNKKKs (including MLK: Mixed Lineage Protein Kinase 2/Slipper; ASK1: Apoptotic signal-regulating Kinase 1; TAK1: TGF- Activated Kinase 1; MEKK1: MEK Kinase1). The kinase cascade is activated by a variety of stressful insults, results in activation of the transcription factors AP-1 (Jun/Fos heterodimers) and Foxo, and causes a variety of tissue-specific and context-specific cellular responses. The JNK phosphatase Puckered (Puc) is a target gene of AP-1 and limits JNK activity in a negative feedback loop. Selected genes that are transcriptionally regulated in response to JNK activation, and that mediate specific physiologic consequences of JNK activation, are listed in green.
