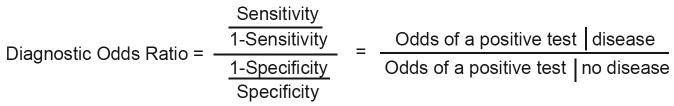Figure 2.
Diagnostic Odds Ratio
(A) The diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) is a measure of the overall accuracy of a positive test and combines a test’s sensitivity and specificity. It is interpreted as the odds of a positive test given disease, divided by the odds of a positive test given no disease. A large DOR of a test means the test has a high sensitivity and specificity for detecting a disease.
(B) The relative diagnostic odds ratio (RDOR) is a ratio of 2 diagnostic odds ratios.
†Covariates that will be examined are the different types of study or sample characteristics such as sample characteristics (i.e., symptomatic, asymptomatic, screening), partial verification bias, among others (See Figure 6).