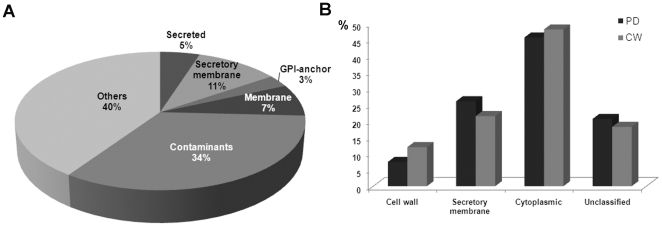
Figure 2. Analysis of the PD-proteome with respect to predicted subcellular localization and its comparison with the CW proteome.
(A) The 1341 proteins of the PD-proteome were classified as secreted proteins, integral membrane proteins processed through the secretory pathway and targeted to Golgi, ER, PM and PD (‘secretory membrane’ proteins), GPI-anchor proteins, non-secreted membrane proteins, contaminant proteins and ‘others’, where others are proteins without membrane association and not predicted to be secreted. The contaminant category includes those proteins predicted to be targeted to chloroplasts, mitochondria and vacuoles. Transmembrane helices (using TMHMM [44]), signal peptides (SIGNALP [83] and SIGNALP-HMM [84]), subcellular location (TARGETP [85]) chloroplast transit peptides (CHLOROP [86]), and GPI-anchoring signals (DGPI [87]) were predicted using software as indicated. (B) GO ‘cellular component’ analysis was used to compare the PD-proteome with the previously reported [23] proteomic data for cell walls from Arabidopsis cell cultures (CW). The main cellular component categories; cell wall, secretory membrane, cytoplasmic and unclassified, proteins, were obtained using GO Slim. (The ‘secretory membrane’ class in B is equivalent to the same class in panel A, although it is defined using different software.) ‘Cytoplasmic’ includes plastid, chloroplast, mitochondria, nuclear, ribosome and cytosol proteins. Unclassified category contains other cytoplasmic, other intracellular and unknown cellular categories. Dark gray bars represent PD-proteome and light gray cell wall proteome.