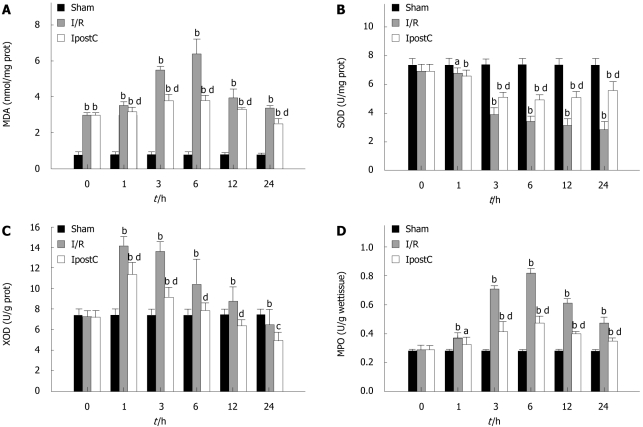
Figure 2.
Gastric oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation after gastric ischemia/reperfusion injury of 3 h of ischemia and 24 h of reperfusion (mean ± SE, n = 36). A: The level of malondialdehyde (MDA); B: The activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD); C: The activity of xanthine oxidase (XOD); D: The activity of myeloperoxidase (MPO). The activity of SOD decreased with the activities of XOD, MPO and the level of MDA increased in the ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) group compared with those of the sham-operated group at 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h. However, ischemic post-conditioning (IpostC) treatment significantly increased the activity of SOD, and decreased the activities of XOD, MPO and the level of MDA at each time. aP< 0.05, bP< 0.01 vs sham group; cP< 0.05, dP< 0.01 vs I/R group.