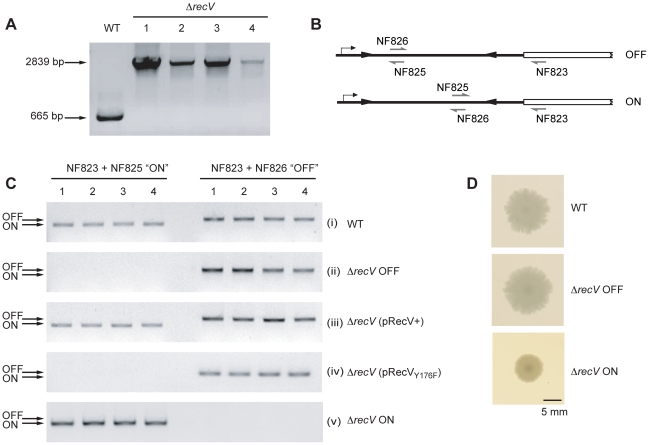
Figure 1. Isolation of ΔrecV mutants. A.
PCR confirmation of recV gene disruption using ClosTron. Primers NF1215+NF1356 flanking the ClosTron target site in recV give a 665 bp product in 630Δerm (WT). After mutagenesis, four erythromycin resistant colonies were tested and a 2839 bp product was amplified, indicative of insertion of the group II intron into recV. These clones were designated ΔrecV 1-4. B. Diagrammatic representation of the cwpV DNA switch orientation-specific PCR assay. Primers NF823+NF826 amplify a product from OFF, whilst primers NF823+NF825 amplify a product from ON. C. Analysis of the orientation of the cwpV DNA switch in C. difficile clones by orientation PCR. (i), products for the ON and OFF orientations are amplified from WT. (ii), all four isolated ΔrecV mutants contain only the OFF orientation of the cwpV DNA switch, therefore these strains are referred to as 630ΔrecV OFF. (iii), complementation of 630ΔrecV OFF using a plasmid encoding recV (pRecV+) reconstituted the switching phenotype. (iv), a recVY176F mutant was unable to complement ΔrecV OFF confirming the key role of this tyrosine residue in RecV activity. (v), ΔrecV(pRecV+) was serially sub-cultured without thiamphenicol selection to enable curing of the pRecV+ plasmid. Four thiamphenicol sensitive colonies were isolated from which only the ON orientation of the cwpV DNA switch could be amplified. These strains were therefore designated ΔrecV ON. D. Colony morphologies of WT and ΔrecV OFF are similar, however ΔrecV ON exhibit a smaller, smoother-edged colony morphology.