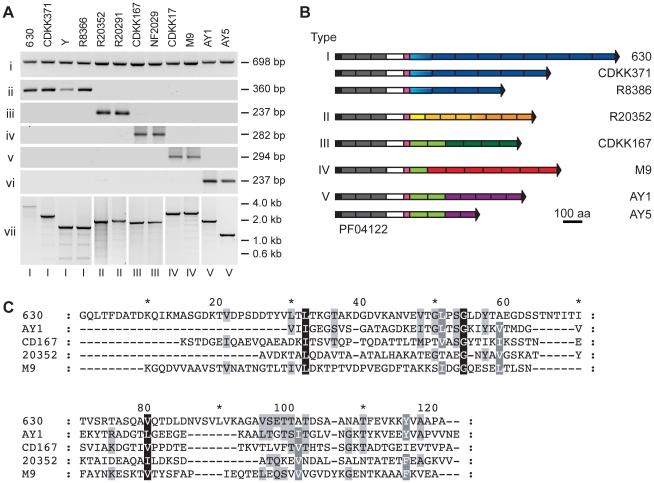
Figure 3. The CwpV C-terminal repeat region is variable across C. difficile strains.
A. PCR analysis of the cwpV locus from diverse strains of C. difficile. Primers used were specific for: i, part of the conserved N-terminal domain (NF654 and NF655) ii, a single type I repeat (NF374 and NF346) iii, a single type II repeat (NF701 and NF702) iv, a single type III repeat (NF796 and NF797) v, a single type IV repeat (NF799 and NF800) vi, a single type V repeat (NF878 and NF879) vii, the entire repeat region, specifically amplified for each type (NF795 with NF373, NF703, NF798, NF801 or NF880). The cwpV type is indicated below each lane and the strain designation above. Details of the primers used are in Table S1. B. Cartoon representation of the eight different discovered configurations of CwpV proteins. For each combination of CwpV type and number of repeats, the repeat region from at least one strain was entirely sequenced. Black, signal sequence; grey, PF04122 cell wall anchoring domains; white, unknown function; pink, serine/glycine-rich region; blue, type I repeats; orange, type II repeats; green, type III repeats; red, type IV repeats, purple, type V repeats. Colour shade represents different sequence variants of a repeat type. Sequence in all strains is almost identical from the signal peptide through to the serine/glycine-rich region. Sequences were deposited at EMBL with accession numbers FM17250-8. C. CLUSTAL multiple sequence alignment of one repeat of each type from strains 630 (type I), 20352 (type II), CD167 (type III), M9 (type IV) and AY1 (type V).