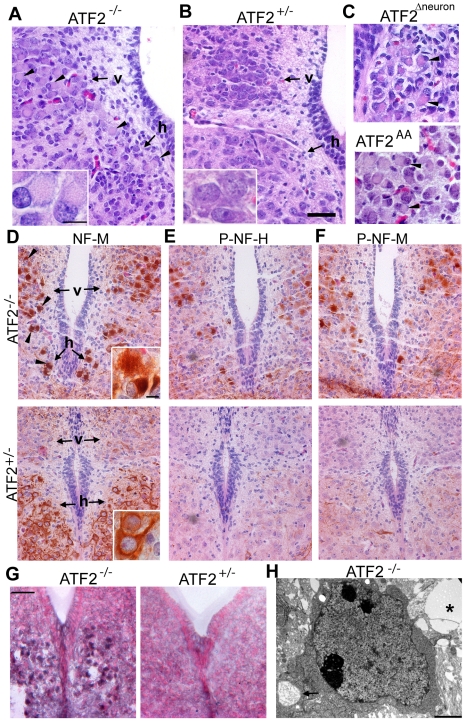
Figure 2. Neuropathological lesions in E18.5 ATF2 mutant motoneurons.
(A, B) H&E stained transversal sections of Atf2−/− and Atf2+/− posterior medulla. Atf2−/− hypoglossal (h) and dorsal vagal (v) motoneurons show ballooned perikarya with eccentrically positioned nuclei (arrowheads). Insets: magnification of dorsal vagal motoneurons. (C) H&E staining of Atf2Δneuron hypoglossal and Atf2AA vagal motoneurons showing the same pathological lesions (arrowheads). (D–F) HRP immunostaining with antibodies against neurofilament M (NF-M), phospho-neurofilament H (P-NF-H, RMO24.9) and phospho-neurofilament M (P-NF-M, RMO8) in Atf2−/− and Atf2+/− posterior medulla. Aberrant NF-M accumulation in the soma of Atf2−/− dorsal vagal and hypoglossal motoneurons is indicated by arrowheads. P-NF-H and P-NF-M are predominantly present in Atf2−/− motoneurons. Insets: magnification of NF-M stained hypoglossal motoneurons. (G) Sudan black B staining shows lipid accumulation in Atf2−/− but not in Atf2+/− hypoglossal motoneurons. Bars: A–G, 100 µm; insets, 25 µm.(H) Transmission electron microscopy photograph of Atf2−/− brainstem shows a lipid droplet near a cell (asterisk), and a cytoplasmic vacuole filled with neurofibrillary material (arrow). Bar: 2 µm.