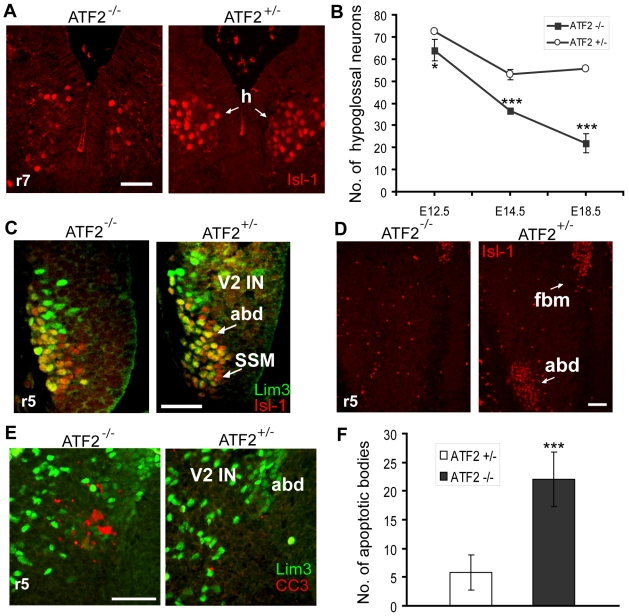
Figure 5. Somatic motoneuron defects in Atf2 − /− embryos.
(A) Isl-1 immunostaining (red) of Atf2−/− and Atf2+/− hypoglossal motoneurons at E14.5 reveal the reduction of Isl-1 positive hypoglossal motoneurons in Atf2−/− embryos. (B) Quantitative analysis of hypoglossal motoneurons (mean number per section ± SD) in serial transversal sections of rhombomere 7 (r7) by Isl-1 immunostaining for E12.5 and E14.5 embryos or by 5-HT immunostaining and hematoxylin counterstaining for E18.5 embryos. Student's two-tailed t-Test, *, p = 0.04; ***, p<0.01; ***; p<0.001. (C) Coimmunostaining of abducens motoneurons with Isl-1 (red) and Lim3 (green) antibodies reveals normal production of these motoneurons in Atf2−/− mice at E10.5 in r5. V2 IN, V2 interneurons, abd, abducens motoneurons, SSM, superior salivatory motoneurons. (D) Complete loss of abducens motoneurons (abd) in Atf2−/− E12.5 embryos as revealed by Isl-1 (red) immunostaining. fbm, facial branchiomotor neurons. (E) Coimmunostaining of abducens motoneurons with Cleaved Caspase 3 (CC3, red) and Lim3 (green) antibodies reveals increased apoptosis in Atf2−/− motoneurons at E11.5. Lim3 strongly labels V2 interneurons and more weakly abducens motoneurons. Bar: 100 µm. (F) Quantitative analysis of apoptotic bodies (mean number per section ± SD) in serial transversal sections of rhombomere 5 at E11.5 reveals increased apoptosis of abducens neurons in Atf2−/− embryos. ***, p<0.01.