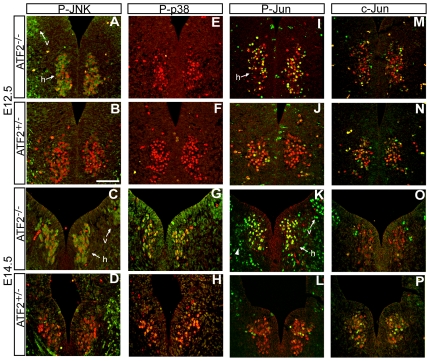
Figure 6. Enhanced phosphorylation of JNK, p38, and c-Jun in Atf2 − /− motoneurons.
Double immunofluorescence staining of Isl-1 (A–P, red) and phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185, green, A–D), phospho-p38 (Thr180/Tyr182, green, E-H), phospho-c-Jun (Ser73, green, I-L) and pan-c-Jun (green, M–P) in hypoglossal (h) and vagal (v) motoneurons at E12.5 and E14.5. (A–D) JNK is hyperphosphorylated in both motoneuron types in Atf2−/− (A and C) compared to Atf2+/− (B and D) embryos at E12.5 and E14.5. (E–H) Phosphorylation of p38 is hardly detectable in Atf2+/− and Atf2−/− at E12.5 (E and F) but significantly increases at E14.5 in motoneurons of Atf2−/− (G) compared to Atf2+/− embryos (H). (I-L) c-Jun is hyperphosphorylated in motoneurons of Atf2−/− (I and K) compared to Atf2+/− (J and L) embryos at E12.5 and E14.5. Strong phosphorylation of c-Jun is notable in hypoglossal and vagal motoneurons at E14.5 and there is a weaker but detectable phosphorylation signal in surrounding cells in Atf2−/− embryos (K, arrowheads). (M, N) High and moderate levels of c-Jun were observed in hypoglossal motoneurons but were indistinguishable between Atf2−/− and Atf2+/− embryos at E12.5. (O, P) At E14.5, Atf2−/− hypoglossal neurons tend to express c-Jun at lower levels than in Atf2+/− neurons; notably some strong c-Jun labeling was detected in some Isl-1 negative cells in Atf2−/−. Bar: 100 µm.