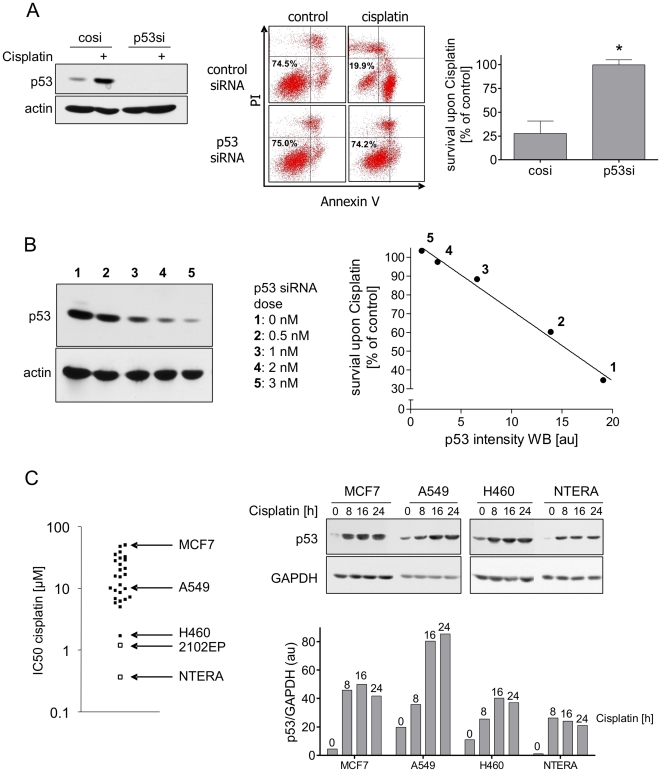
Figure 1. Hypersensitivity of NTERA-2D1 is entirely dependent on p53.
(A) siRNA-mediated knockdown of p53 rescues NTERA-2D1 from Cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Cells were transfected with siRNA and incubated for 48 h prior to Cisplatin treatment (16 h). Left panel: verification of p53 knockdown by Western Blot analysis. Middle and right panel: cells were stained with Annexin-V/FITC and PI and analyzed by flow cytometry. Graph reflects means ±SD of survival after Cisplatin relating to corresponding controls from 5 experiments (P = 0.0003). (B) Cisplatin-induced apoptosis correlates with the amount of p53 protein (densitometric values). Cells were transfected with indicated amounts of p53-targeting siRNA 48 h before Cisplatin treatment (16 h) and analyzed by Western Blot. (C) Hypersensitivity of NTERA-2D1 is not due to extraordinary high levels of p53. Left panel: Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of Cisplatin to determine IC50 in a panel of 28 cell lines (the two TGCT cell lines NTERA-2D1 and 2102EP are indicated by open squares) using MTT assay. Three cell lines (MCF-7, A549, H460) with differing Cisplatin sensitivity were chosen to compare p53 protein levels with NTERA-2D1. Right panel: Cells were treated with Cisplatin for indicated times and whole protein lysates were then applied to Western Blot analysis. Graph reflects intensity of p53 bands determined by densitometry relating to the amount of GAPDH.