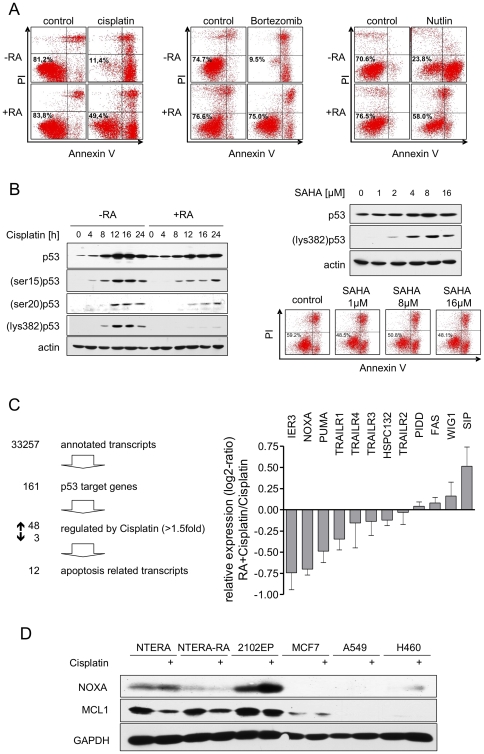
Figure 5. Short-term differentiation of NTERA-2D1 by RA causes a loss in hypersensitivity.
Cells were partially differentiated with RA for 48 h prior to drug treatment. (A) Short-term differentiation rescues NTERA-2D1 from cell death induced by DNA damaging and DNA damaging independent agents. Cells were treated with Cisplatin, Nutlin-3 or Bortezomib, respectively for 16 h, stained with Annexin-V/FITC and PI and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Posttranslational modifications seem to play a minor role in loss of hypersensitivity upon short-term differentiation. Left panel: differentiated and control cells were treated with Cisplatin for indicated times and analyzed by Western Blot. Right panel: upon differentiation with RA, cells were pre-incubated with indicated concentrations of histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA for 2 h followed by Cisplatin treatment. Cells were stained with Annexin-V/FITC and PI and analyzed by flow cytometry and protein levels of p53 and acetylation on lysine 382 were analyzed by Western Blot. (C) Expression level of NOXA upon Cisplatin is reduced in NTERA-2D1 cells pre-treated with RA. Differentiated and control cells were treated with Cisplatin for 6 h, RNA was isolated and applied to microarray analysis to assess global gene expression. Left panel: selection criteria for Cisplatin-induced p53 target genes related to apoptosis. Right panel: expression levels of the 12 apoptosis-related p53 targets upon Cisplatin were compared to cells differentiated prior to Cisplatin treatment. Graph reflects means ±SD from 3 experiments. (D) NOXA basal and Cisplatin-induced protein levels are higher in non-differentiated NTERA-2D1 and 2102EP cells than those of differentiated NTERA-2D1 (NTERA-RA) or other tumor cell lines. Cells were treated with Cisplatin for 16 h and harvested. Lysates were then used for Western Blot analysis.