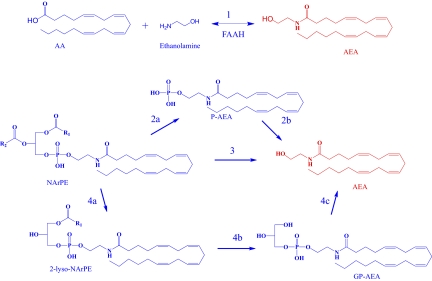
Fig. 1.
Pathways for anandamide (AEA) biosynthesis. (i) FAAH catalyzes the condensation of arachidonic acid (AA) and ethanolamine to form anandamide (pathway 1). (ii) A type-C phospholipase hydrolyzes NArPE to phosphoanandamide (pAEA) (pathway 2a). PTPN22, Src homology 2 domain-containing inositol-5-phosphatase 1, or other uncharacterized phosphatases dephosphorylate pAEA to form AEA (pathway 2b). (iii) The metallo-β lactamase, N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine, hydrolyzes NArPE to form AEA through a one-step reaction (pathway 3). (iv) The serine hydrolase, abhd4, sequentially removes acyl groups from NArPE to form lyso-NArPE and then, GP-AEA (pathway 4 a and b). The metal-dependant phosphodiesterase, GDE1, hydrolyzes GP-AEA to form AEA (pathway 4c). Details in Ueda and Tsuboi (11) and Simon and Cravatt (14). Anandamide is highlighted in red.