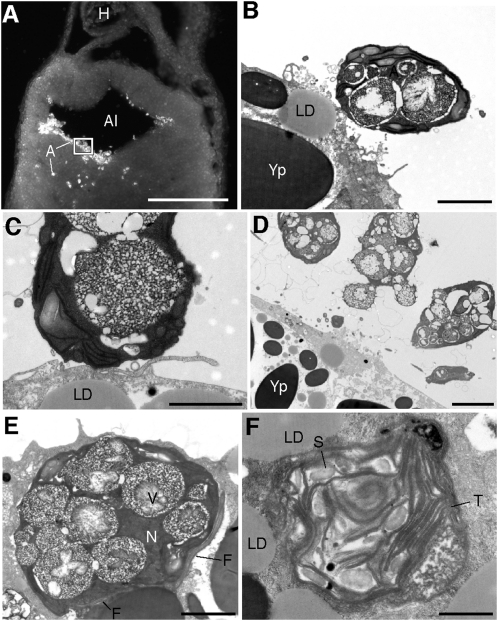
Fig. 4.
Algal cells within the alimentary canal during the process of cellular invasion. (A) Fluorescent image of a coronal vibratome section through a Stage-35 embryo showing an aggregation of algae (A) inside the alimentary canal (Al) and invading the surrounding endoderm. (B–F) TEM images from boxed region in A. (B–D) Algal cells in the alimentary canal, adjacent to salamander endoderm. (E) Algal cell inside endodermal cell of the alimentary canal containing many large vacuoles (V) and paired flagella (F). (F) Free thylakoid membranes (T) and starch granules (S) inside cytoplasm of host cell shown in E. H, heart; LD, lipid droplet; N, nucleus; Yp, yolk platelet. (Scale bars: 1 mm in A; 2 μm in B and C; 5 μm in D; 2 μm in E; 1 μm in F.)