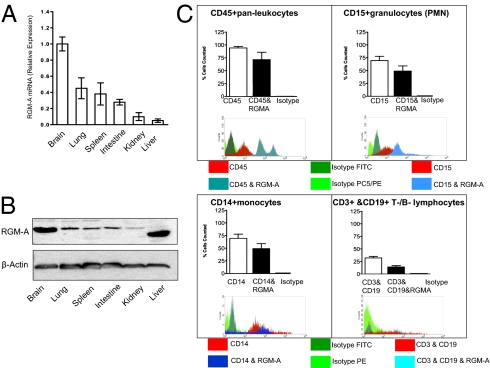
Fig. 1.
RGM-A is expressed outside the CNS postdevelopmentally. (A) RGM-A mRNA in murine tissues quantified by quantitative real-time RT-PCR compared with levels of RGM-A mRNA expression present in the murine brain. Along with lymphatic tissue such as spleen, pronounced RGM-A mRNA levels were detected in organs hosting an intrinsic immune compartment, including the brain (microglia), lungs (alveolar macrophages), and intestines (Peyer's patches). (B) Western blot analysis of RGM-A protein expression in pooled murine tissues compared with levels of expression in the brain. Values correspond to relative RGM-A mRNA levels. All data are mean ± SEM; n = 5. (C) FACS analysis verified the expression of RGM-A by leukocyte subsets including CD15+ granulocytes (PMNs), CD14+ monocytes, CD3+ T lymphocytes, and some CD19+ B lymphocytes (PMNs). Isotype controls demonstrated no relevant signal.