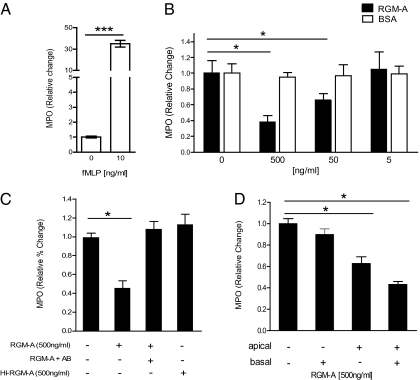
Fig. 3.
RGM-A inhibits active PMN migration in vitro. (A) fMLP (10 ng/mL) induced chemotaxis-dependent migration of PMNs through a CaCo epithelial cell monolayer. 1 × 106 granulocytes were placed in the apical compartment and transmigration of PMNs measured after 60 min. Measurement of MPO as representative marker was used to quantify basolateral PMN transmigration. (B) PMN transmigration in the presence of distinct concentrations of RGM-A or BSA, showing suppression of PMN migration by RGM-A in a dose-dependent fashion. (C) RGM-A–specific effects on PMN migration in the presence of RGM-A antibody (AB) and heat-inactivated RGM-A (HI-RGM-A). (D) PMN transmigration in the presence of distinct concentrations of RGM-A in the apical compartment, basolateral compartment, or both compartments of a transmigration chamber. All data are mean ± SEM; n = 6 per group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.