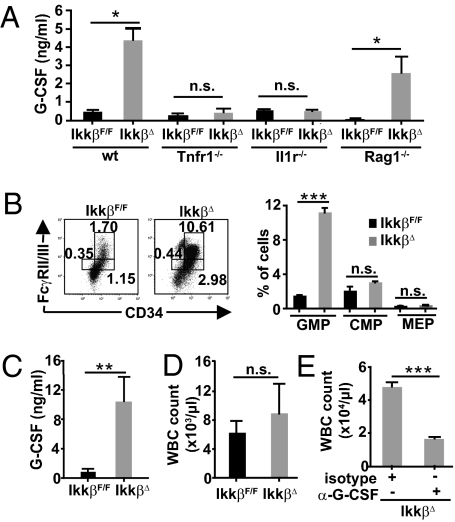
Fig. 4.
G-CSF is markedly increased and is responsible for GMP expansion and consecutive neutrophilia in IkkβΔ mice. (A) G-CSF levels in the plasma from IkkβF/F, IkkβΔ, Tnfr1−/−, and IkkβΔ/Tnfr1−/−, Il1r−/−, and IkkβΔ/Il1r−/− double KO mice as well as Rag1−/− and IkkβΔ/Rag1−/− compound mutants 21 d after poly(I:C) administration. Data are mean ± SE from at least six mice (*P < 0.05). (B) Representative FACS plots and mean numbers of myeloid progenitors in IkkβF/F and IkkβΔ mice 21 d after poly(I:C) administration demonstrate a significant increase of GMP in IkkβΔ mice determined by FcγRII/III and CD34 expression in Lin−/IL-7Rα−/Sca-1−/c-Kit+ cells. Data are mean ± SE from three mice (***P < 0.0001). (C and D) Plasma G-CSF levels (C) and WBC counts (D) of IkkβF/F and IkkβΔ mice 5 d after poly(I:C) administration. Data are mean ± SE from at least five mice (**P < 0.01). (E) WBC count of IkkβΔ mice 21 d after poly(I:C) administration that had been injected daily with rat α-G-CSF or a respective isotype control. Data are mean ± SE from four mice (***P < 0.0001).