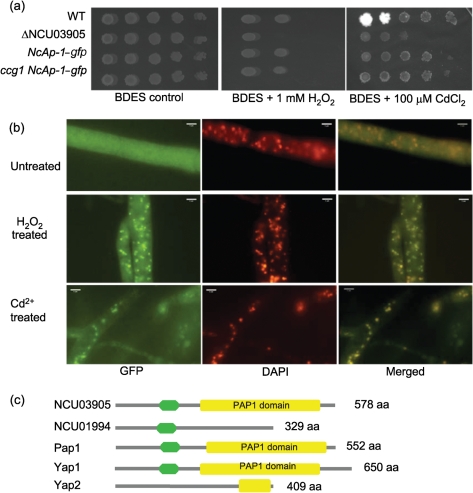
Fig. 2.
Complementation of ΔNcAp-1 and localization of NcAp-1–GFP. (a) Comparison of the phenotype of the WT (FGSC 2489), the NcAp-1 mutant (ΔNCU03905) and ΔNcAp-1 complemented strains (NcAp-1–gfp and ccg1 NcAp-1–gfp) exposed to 1 mM H2O2 or 100 μM Cd2+ using a dilution series of conidial suspensions (from left to right: 105, 104, 103, 102, 101). Plates were incubated at 25 °C for 2 days and then evaluated for growth. (b) NcAp-1–GFP localization in a ΔNcAp-1 (his-3 : : NcAp-1–gfp) strain grown on minimal medium (untreated, upper panels), after treatment with 30 mM H2O2 (H2O2 treated, centre panels) or 10 mM CdCl2 (Cd2+ treated, lower panels). The left-hand panels show GFP fluorescence (NCAp-1–GFP), while the centre panels show nuclear 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining. The right-hand panels show merged GFP and DAPI images. (c) Domain prediction of Yap1, Yap2, Pap1, NCU03905 (NcAp-1) and its closest paralogue NCU01994. Green, bZIP motif; yellow, PAP1 domain.