Figure 4.
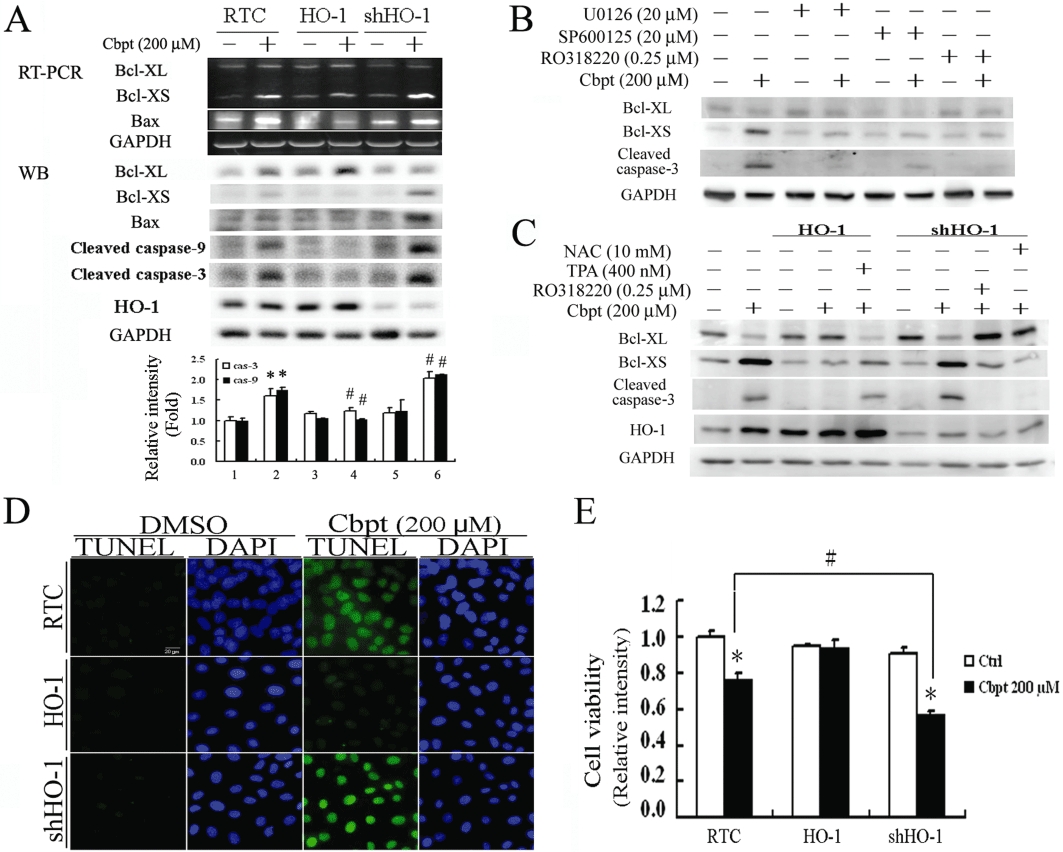
Rescue of carboplatin (Cbpt)-mediated apoptosis by haem oxygenase (HO)-1 overexpression through inhibition of apoptosis-related molecules. (A) Renal tubular cell (RTC) variants were treated with 200 µM carboplatin for 4 h for the reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis of Bcl-XL/XS and Bax, and for 18 h for the Western blot analysis of cleaved caspses-3 and -9. The lower panel shows the intensity of bands from the Western blots by densitometry. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (B) RTC were pretreated with U0126, SP600125 and R0318220, which are inhibitors of the extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK)/Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/protein kinase C (PKC) pathways involved in nuclear factor of activated T-lymphocyte-3 activation. The treatment continued for 1 h prior to a 200 µM carboplatin treatment for 18 h. Cell lysates were harvested for the Western blot analysis of Bcl-XL/Bcl-XS, and the cleaved form of caspase-3. (C) The effect of the PKC pathway in carboplatin-mediated Bcl-X alternative splicing was examined in cell variants pretreated with a PKC activator or inhibitor. RTC with either HO-1 overexpression or knockdown were pretreated with TPA (a PKC activator) or R0318220 (a PKC inhibitor), for 1 h prior to a 200 µM carboplatin treatment for 18 h. Cell lysates were analysed by Western blots for levels of Bcl-XL and Bcl-XS. A representative result of three separate experiments is shown. Cell variants treated with 200 µM carboplatin for 24 or 36 h were analysed for cell apoptosis (D) and cell viability (E) respectively. A representative result of three separate experiments is shown. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, significantly different from its respective RTC variants; #P < 0.05, significantly different from RTC with additional carboplatin treatment). Ctrl, control; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DMSO, dimethyl sulphoxide; NAC, N-acetylcysteine; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling.
