Figure 4.
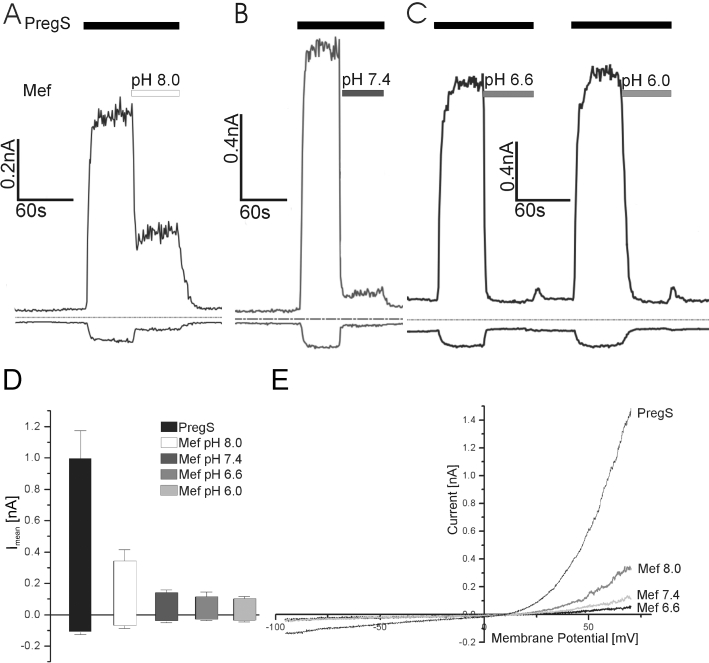
pH-dependence of mefenamic acid on the inhibition of TRPM3-mediated currents. (A) Time course of TRPM3 current at membrane potentials of −80 (lower trace) and +80 mV (upper trace); the pH value of the extracellular solution was 8 before the mefenamic acid (25 µM) was added. (B) Time course of TRPM3 current at membrane potentials of −80 and +80 mV; the pH value of the extracellular solution was 7.4 before the mefenamic acid (25 µM) was added. (C) Time course of TRPM3 current at membrane potentials of −80 and +80 mV; the pH values of the extracellular solution were 6.6 and 6.0 before the mefenamic acid (25 µM) was added. (D) Statistical analysis of experiments performed at pH 8 (n = 9), pH 7.4 (n = 19), pH 6.6 (n = 10) and pH 6 (n = 9). (E) Current–voltage relationship from experiments shown in (A–C). Although the inward currents were almost completely inhibited, the block of the outward current was dependent on the pH values.
