Figure 1.
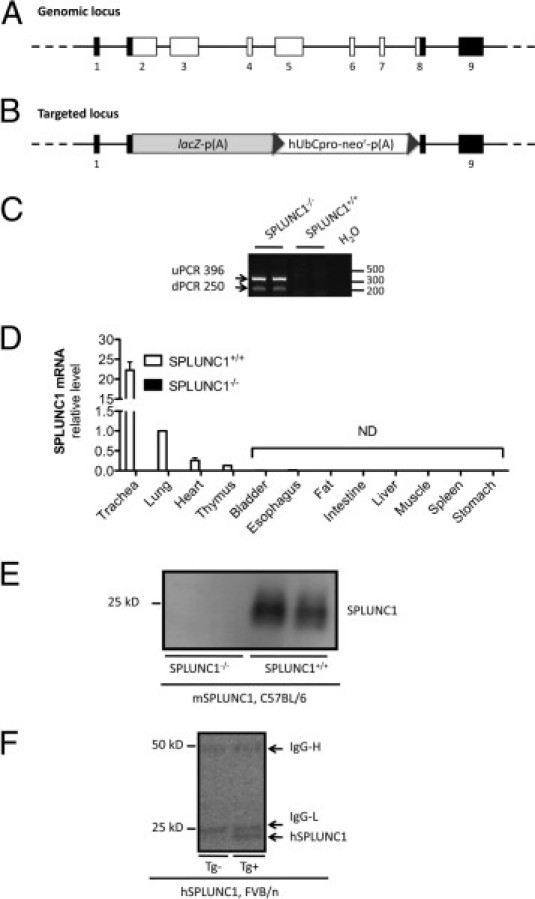
Generation of SPLUNC1−/− mice and detection of SPLUNC1 in SPLUNC1−/− and hSPLUNC1 transgenic mice. A: Schema of the SPLUNC1 genomic locus. Black squares, noncoding exons; white squares, coding exons. B: Schema of the targeted locus. Homologous recombination resulted in replacement of SPLUNC1 genomic region (chromosome 2 deletion from 153,969,486 to 153,973,826) via expression-selection cassette containing lacZ-neomycin resistance genes. lacZ, coding sequence for β-galactosidase from the E. coli lacZ gene. p(A), polyadenylation signal; neo′, coding sequence for neomycin phosphotransferase; hUbCpro, promoter from human ubiquitin C gene; uPCR, upstream PCR; dPCR, downstream PCR. C: PCR confirmation of targeting construct orientation in chromosome 2 of SPLUNC1−/− mice. uPCR, detection of β-galactosidase (upstream) in mouse genomic DNA; dPCR, detection of neomycin (downstream) in mouse genomic DNA. No amplification was detected in SPLUNC1+/+ mice. D: Tissue SPLUNC1 mRNA levels. Various tissues were obtained from SPLUNC1+/+ or SPLUNC1−/− mice (n = 3 per group). Data are given as mean (SEM) and normalized to wild-type lung tissue expression. ND, not detectable. E: mSPLUNC1 protein was detected using Western blot analysis using sheep anti-mouse SPLUNC1 antibody in BAL fluid (30 μL per lane) from SPLUNC1+/+ but not SPLUNC1−/− mice. F: hSPLUNC1 protein was detected using Western blot analysis using mouse anti-human SPLUNC1 antibody in BAL fluid (30 μL per lane) from hSPLUNC1 transgene-positive (Tg+) but not transgene-negative (Tg−) mice. The 50 and 25 kDa bands represent mouse IgG heavy (IgG-H) and IgG light (IgG-L) chains, respectively.
