Figure 7.
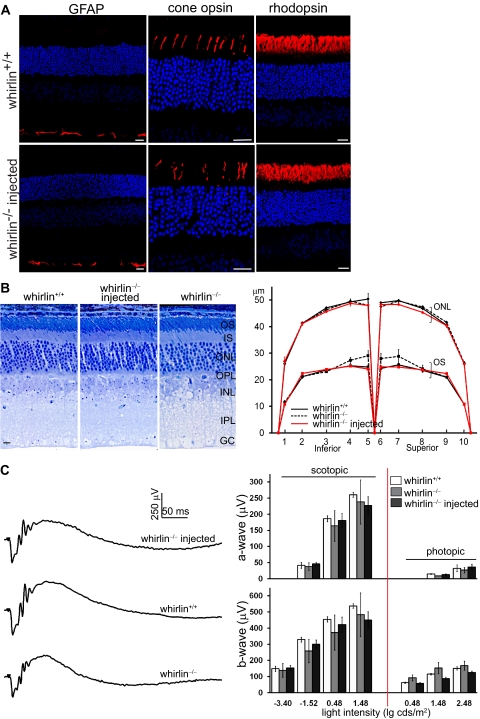
No defects found in the retinal morphology or function at 6 months post injection of AAV-whirlin. (A) Immunostaining of GFAP, cone opsins (mixed blue and green opsins), and rhodopsin in the wild-type retina (whirlin+/+, upper panels) and the whirlin−/− retina injected with AAV-whirlin (lower panels). No mislocalization of rhodopsin and cone opsins and no changes in GFAP expression were observed in the injected whirlin−/− retina, compared with the age-matched wild-type retina. Scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Histologic analysis of the injected whirlin−/− retina. Left: representative retinal sections from whirlin+/+, whirlin−/−, and injected whirlin−/− mice. Scale bars, 10 μm. Right: measurement of the outer segment length (OS) and the outer nuclear layer thickness (ONL) along the retinal vertical meridian in whirlin+/+, whirlin−/−, and injected whirlin−/− mice. The number of retinas measured at each position in each group is between 3 and 6. The error bar represents the SEM. (C) ERG tests on the injected whirlin−/− eye. Left: representative scotopic ERG tracings from whirlin+/+, whirlin−/−, and injected whirlin−/− mice at the light intensity of 0.48 lg cds/m2. Right: bar charts showing the amplitude of a-wave and b-wave of scotopic and photopic ERGs at different light intensities in whirlin+/+, whirlin−/−, and injected whirlin−/− mice. The number of eyes measured at each light intensity in each group is between 3 and 6. The error bar represents the SEM.