Fig. 2.
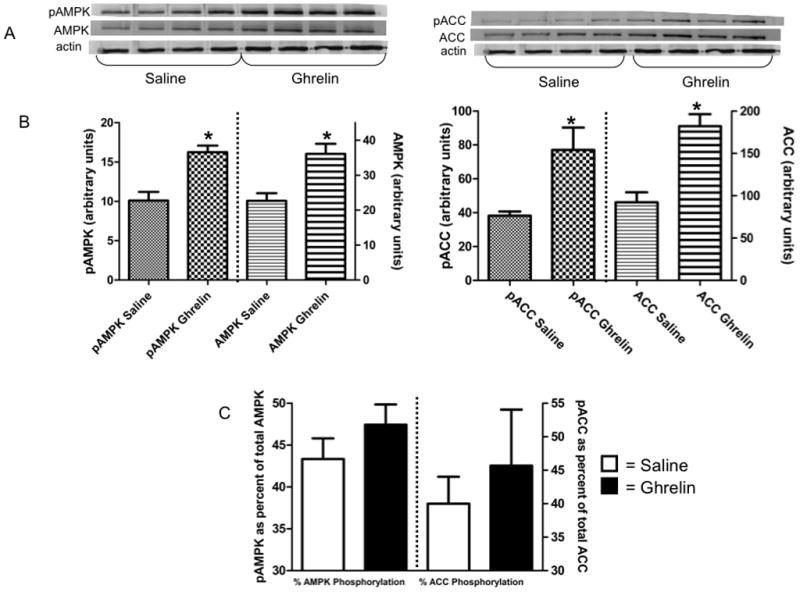
In total hypothalamus homogenate from normophagic summer animals, animals injected IP with ghrelin have statistically higher (p≤0.05) levels of total and phosphorylated AMPK and ACC compared with saline injected controls. (A) Representative Western blots of saline-injected (n=4) and ghrelin-injected (n=4) animals. Blots were probed for pAMPK and pACC, then stripped and reprobed for total AMPK and ACC with β-actin for a loading control. (B) Levels (normalized against actin) of phosphorylated vs. total AMPK and phosphorylated vs. total ACC. (C) Ratio of phosphorylated to total AMPK and ACC in hypothalamus after saline or ghrelin injection. * indicates significance between saline and ghrelin-injected animals at p≤0.05 (Student t-test).
