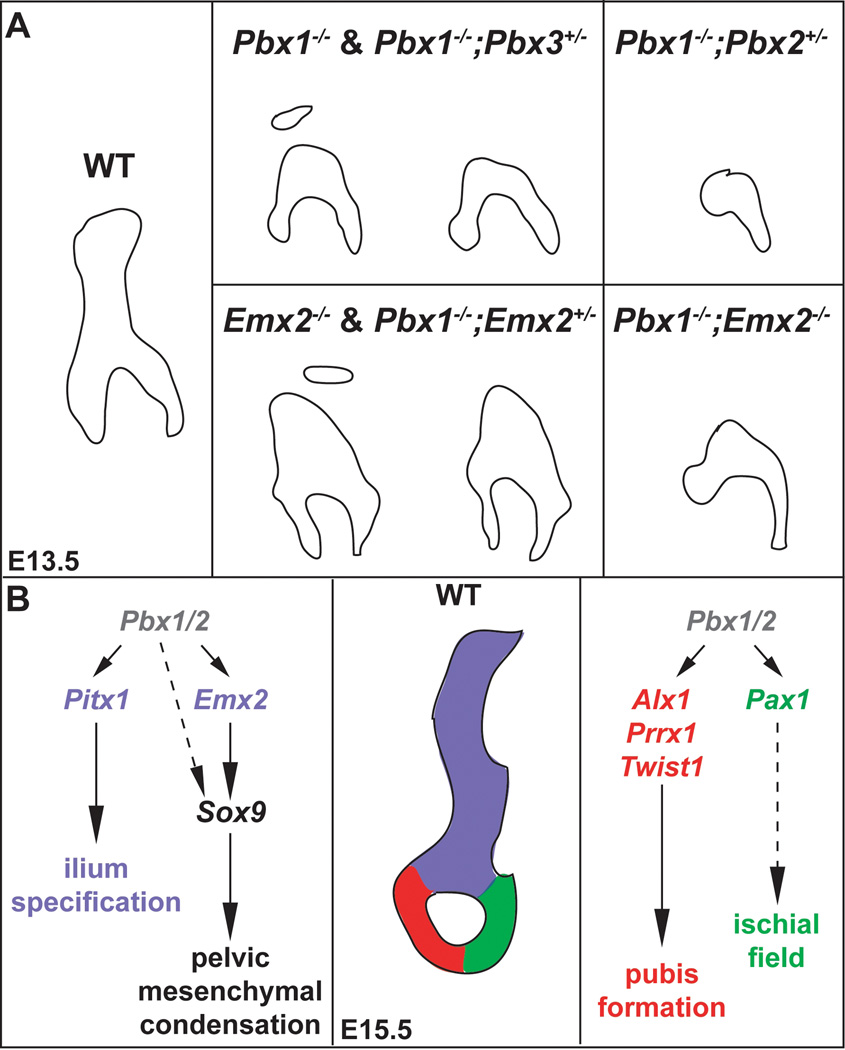
Fig. 9.
Summary and model of Pbx family member and Emx2 genetic functions during pelvic development. A: Illustrations depicting the phenotypes of the compound Pbx family member and Pbx1;Emx2 mutants analyzed in this study (see text for details). B: Model of Pbx family member and Emx2 genetic functions during pelvic girdle formation. (center panel) An E15.5 WT pelvis demonstrating the three distinct bony elements in color (blue – ilium, red – pubis, green – ischium). These colors reflect the genes involved in the formation of each structure, as depicted in the left and right panels. (left panel) Pbx1/Pbx2 hierarchically regulate Pitx1 and Emx2 during the specification and condensation of the ilium (blue), respectively. Dashed arrow indicates a potential control of Sox9 directly by Pbx family members. (right panel) Pbx1/Pbx2 hierarchically regulate genes involved in pubis development (red), such as Alx1, Prrx1, and Twist1, and ischial field expression (dashed green arrow), such as Pax1.