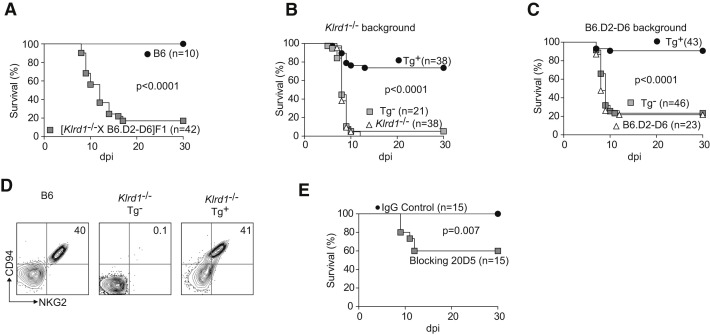
Figure 3.
CD94 Is Essential for Resistance to Mousepox
(A) Wild-type B6 or [B6.D2-D6 × CD94-deficient] F1 mice were infected with ECTV and survival was monitored.
(B) CD94 transgenic (Tg+) and nontransgenic (Tg−) CD94-deficient × [CD94-deficient × B6-CD94Tg] F1 littermate mice and parental CD94-deficient mice were infected with ECTV and survival was monitored.
(C) Transgenic (Tg+) and nontransgenic (Tg−) B6.D2-D6 × [B6.D2-D6 × B6-CD94Tg] F1 littermate mice and parental B6.D2-D6 mice were infected with ECTV and survival was monitored.
(D) Flow cytometric analysis of white blood cells from the indicated mice. Plots are gated on NKp46+CD3− NK cells. Staining for CD94 and NKG2 is shown.
Data are representative of three similar experiments.
(E) B6 mice were treated with 150 μg 20D5HCmIgG1-Q mAb or an isotype-matched control mAb, infected with ECTV and survival monitored.
Data are cumulative from three independent experiments.