Fig. 1.
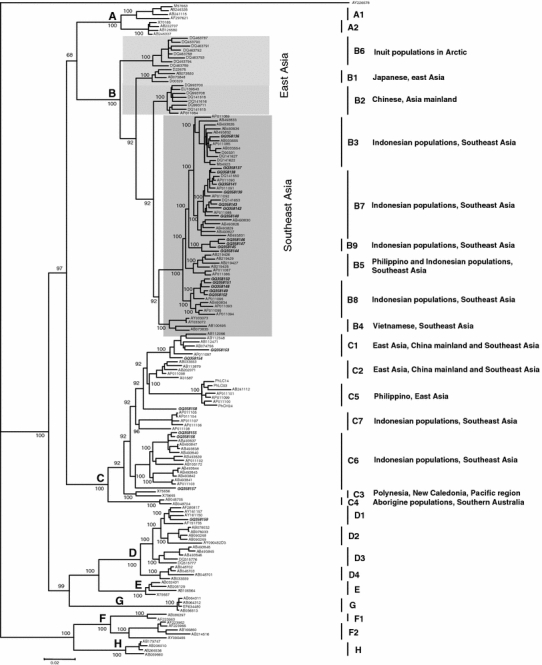
Phylogenetic analysis of 24 new whole HBV genome sequences reveals a novel HBV/B subgenotype. A phylogenetic tree was constructed from 24 whole genome sequences generated in the present study (bold and italic), and 141 representative sequences retrieved from the GenBank database (8 HBV/A [A1 4, A2 4], 58 HBV/B [B1 4, B2 8, B3 12, B4 4, B5 6, B6 8, B7 11, and B8 5], 38 HBV/C [C1 5, C2 5, C3 2, C4 2, C5 7, C6 12, C7 5], 18 HBV/D [D1 4, D2 5, D3 5 and D4 4], 4 HBV/E, 7 HBV/F [F1 2, F2 5], 4 HBV/G and 4 HBV/H). Genetic distances were calculated by the six-parameter method [40], with the wooly monkey strain (WMHBV) AY2266578 as an outgroup. The length of the horizontal bar indicates the number of nucleotide substitutions per site, and the posterior probability values are indicated at the roots of the tree. The tree demonstrates a clear distinction between the East Asia and Southeast Asia HBV/B subgenotype groups (the non-recombinant type [42] is indicated by light shading, and the recombinant type by darker shading) and reveals that 17 out of the 24 new sequences belong to HBV/B (1 B3, 7 B7, 5 B8, and 4 belonging to a previously unidentified but distinct cluster), 5 HBV/C (2 C1 and 3 C6), and 1 HBV/D (D1). The unidentified cluster was separated from other HBV/B Southeast Asia isolates, with a good value for posterior probability, suggesting that it is of a novel HBV/B subgenotype, designated B9. Of the sequences retrieved from GenBank, 5 reported previously as B3 (AB493827, AB493828, AB493829, AB493830, and AB493831) [55] clustered with B7. Furthermore, one previously unidentified isolate (AB493834) [55] was found to cluster with B8
