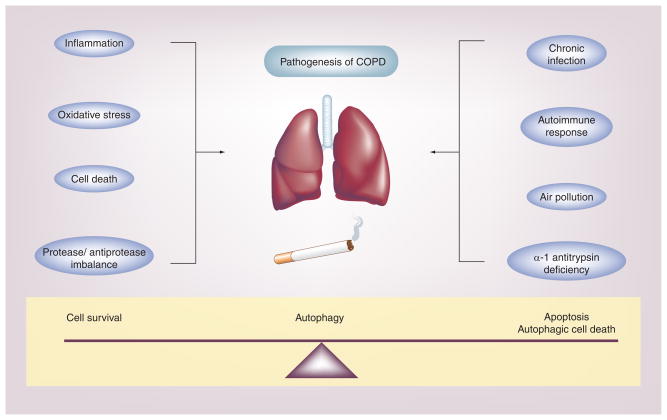
Figure 1. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a multifactorial disease involving airflow limitation, bronchitis and emphysema, induced primarily by cigarette smoking.
The molecular mechanisms governing the pathogenesis of COPD remain unclear, but may involve several factors. Of these, oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and protease/antiprotease imbalance may play critical roles. COPD pathogenesis can also be influenced by additional factors, such as chronic exposure to air pollution of microbial pathogens, genetic factors, such as α-1 antitrypsin deficiency, and autoimmune responses. Autophagy, a fundamental homeostatic process, may play a critical role in COPD pathogenesis by influencing epithelial cell fate in response to environmental stress (i.e., cigarette smoke) [19].
COPD: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.