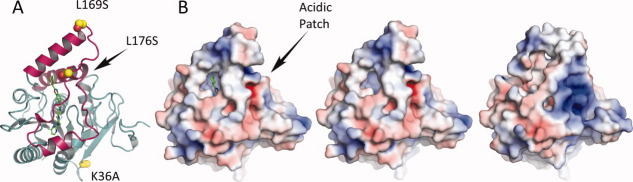
Figure 5.
Enabling mutations and electrostatics. A: Location of the enabling mutations. Leu169Ser and Leu176Ser are located in the lid sub-domain (magenta) and prevent protein aggregation. Lys36Ala is located on the loop between β2 and β4 and would make interactions with a symmetry mate if present in the wild-type protein. B. Electrostatic potential of MGL contoured at ±5 kT (red, negative potential; blue, positive potential). Orientation of the protein is identical to the one in panel A. MGL's lid-domain in the closed conformation (B, left) shows a somewhat reduced hydrophobic character as compared to the apo form of MGL (PDB ID 3JHU ) in the open conformation (B, right). The reduced hydrophobic character and the presence of the acidic patch on the right side of the molecule could point to a potential mechanism for dissociation from the membrane during catalysis. Remarkably, replacement of the enabling mutations with wild-type residues (B, middle) does not appear to have a discernable effect on the electrostatic potential of the protein.