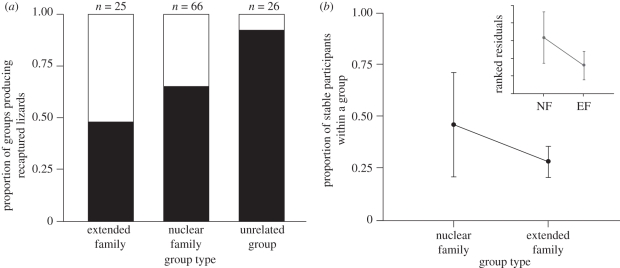
Figure 4.
(a) Relative proportion of groups with juveniles by aggregation type shows higher recapture probability of lizards from groups containing kin than from unrelated groups (group type effect: χ22 = 10.45, p = 0.005; see text for full model details). Sample sizes above the bars indicate the total number of groups of each type (n = 117 groups total). White bar, recapture; black bar, no recapture. (b) Proportion of stable group participants by group type, in groups with both recapture data and juveniles (n = 24 groups). Inset graph displays the Wilcoxon signed-rank test using ranked residuals to remove a group size effect, showing that group stability is higher in groups with nuclear family members (χ21 = 7.38, p = 0.007). Error bars represent ±1 s.d.