Figure 5. Measuring BoNT/A activity in cell based assays using BoNT/A cleavage-sensitive (BACS) antibodies.
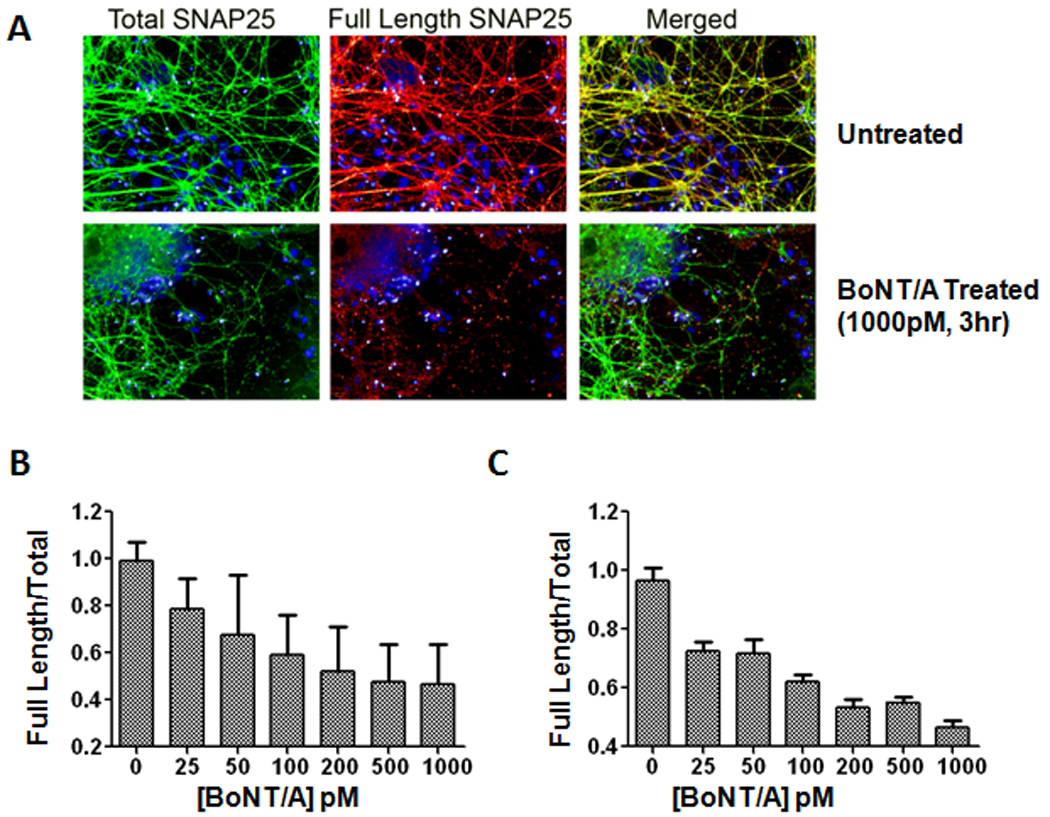
(A) ES cell-derived motoneurons were fixed and immunolabeled with antibodies to detect total SNAP-25 (N-terminal specific antibody labeling) (green) and full length SNAP-25 (BACS antibody labeling) (red). The nuclei in all images were labeled with Hoechst dye (blue). After a 3 hr BoNT/A intoxication, truncated SNAP-25 was recognized by total SNAP-25 antibodies, but not by BACS antibodies, which resulted in a reduction in red fluorescence. (B) High content imaging assay for measuring BoNT/A activity. ES cell-derived motoneurons were treated with a range of BoNT/A concentrations (0–1000 pM) and following 3 hr incubation were fixed and stained with total SNAP-25 and BACS antibodies as described in part A. (C) Licor imaging assay for measuring intracellular BoNT/A activity. Cells were treated with BoNT/A (0–1000 pM), incubated for 3 hrs and fixed and stained with the antibody combinations described above. The measured dose response in both high content imaging and Li-Cor imaging assays correlated well with BoNT/A concentrations. For each condition, images from 6 fields/well were acquired with the script calculating the integrated fluorescence intensities in whole cell regions. Error bars represent standard errors of the averages.
