Figure 2. Cervical spinal 5-HT7 receptor activation facilitates phrenic burst amplitudes in anaesthetized rats.
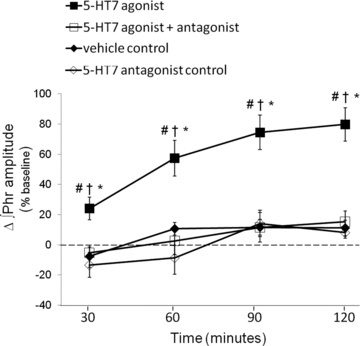
Comparisons of integrated phrenic burst amplitudes from spinally treated rats; values are expressed as a percentage change from baseline. Spinal 5-HT7 receptor agonist (▪, AS-19; 10 μm, 3 × 5 μl) significantly increased phrenic burst amplitude (80%± 11%, n = 7; P < 0.05) compared to vehicle treated rats (♦, 11%± 5%, n = 7). An injection of a 5-HT7 receptor antagonist (□, SB269970, 5 mm, 7 μl) blocked 5-HT7 agonist-induced PMF at all time points (30 min: −5 ± 4%, P = 0.007; 60 min: 3 ± 9%, P < 0.001; 90 min: 15 ± 7%, P < 0.001; 120 min: 15 ± 7%, P < 0.001; n = 6). To control for drug effects, SB269970 (⋄, 5-HT7 antagonist control, n = 4) was given alone; it had no effect on phrenic burst amplitude at any time. #Different from vehicle; †different from 5-HT7 agonist + antagonist; *different from 5-HT7 antagonist control; RMANOVA, P < 0.05.
