Figure 2.
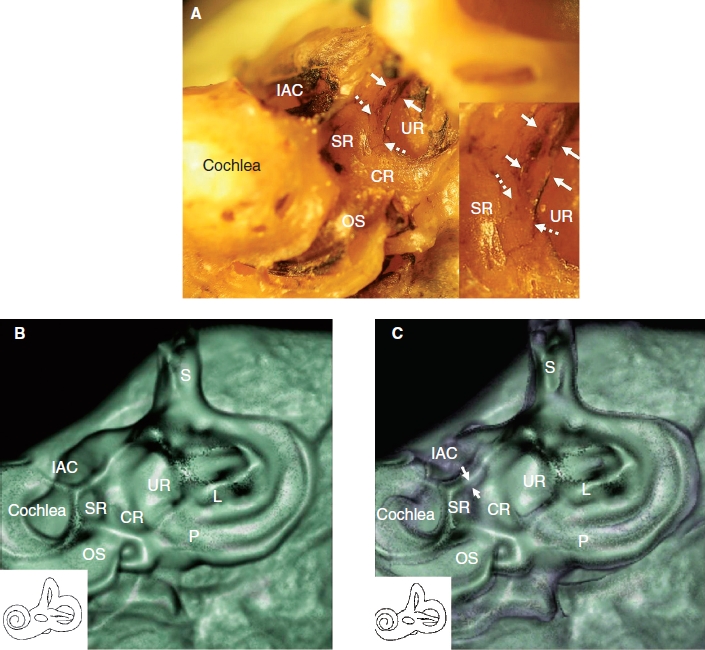
Direction of CT examination and CT findings in the cadaver. (A) This position of the temporal bone is suitable to obtain more accurate CT images of the saccule, saccular duct, and endolymphatic sinus. Note that the remnant membranous labyrinth, shown in black, is visible. Insert: Higher magnification of the groove of the saccular duct (white dashed arrows) and endolymphatic sinus (white arrows). (B) The sulciform groove-like 3D CT image of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus of the same specimen as in (A), which was examined in the same direction as in (A) with a bone CT window level. (C) The same specimen as in (A) with CT window levels of bone and soft tissue. The membranous composition of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus in purple (white arrows) are surrounded by the artificial shadow of a rendering effect. The details of the aspects are consistent with macroscopic specimens. Purple indicates soft tissue. CR, cochlear recess; IAC, internal auditory canal; L, lateral semicircular canal; OS, osseous spiral lamina; P, posterior semicircular canal; S, superior semicircular canal; SR, saccular recess; UR, utricular recess.
