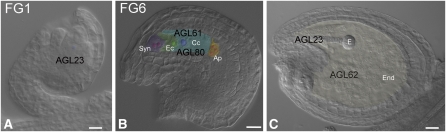
Figure 2.
Type I MADS Box Genes Control Female Gametophyte and Seed Development.
Differential interference contrast microscopy images of wild-type Arabidopsis developing ovules and seeds: female gametophyte at stage1 (A), female gametophyte at stage 6 (B), and embryo at globular stage (C). Type I MADS domain proteins are indicated related to their function in the corresponding developmental stages and their function in a specific process. AGL23 (A) is involved in the early phase of gametogenesis (M. Colombo et al., 2008). The agl23 embryo sac arrests at FG1. AGL23 also regulates chloroplast biogenesis, which occurs in the embryo at the globular stage (C) (M. Colombo et al., 2008). AGL80 ([B] and [C]) disruption affects central cell differentiation (Portereiko et al., 2006). AGL80 interacts with AGL61, and genetic evidence supports the yeast two-hybrid assays, as agl61 embryo sacs develop defective central cells (Bemer et al., 2008; Steffen et al., 2008). AGL62 (C) suppresses cellularization and promotes nuclear proliferation during early endosperm development (Kang et al., 2008). The role of AGL80 during endosperm development has yet to be clarified. Ap, antipodal cells; Cc, central cell; Ec, egg cell; E, embryo; End, endosperm; Syn, synergid cells. Bars = 20 μm.