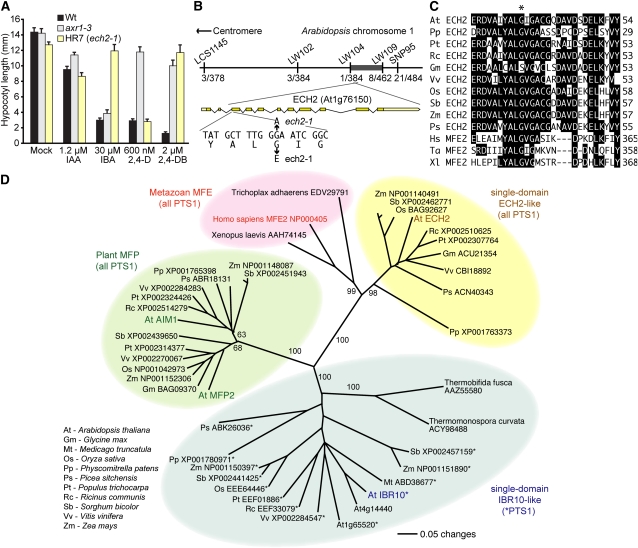
Figure 1.
ECH2 Is Required for Hypocotyl IBA Response.
(A) Mean hypocotyl lengths (+se; n ≥ 14) of dark-grown wild type (Wt), axr1-3, and isolate HR7 (ech2-1) on various natural and synthetic auxins.
(B) Recombination mapping with the indicated markers (see Supplemental Table 2 online) localized HR7 to a 2-Mb region on chromosome 1 (dark bar) containing 592 predicted genes between LW104 and LW109 with 1/384 and 8/462 flanking recombinants. Examination of the ECH2 (At1g76150) gene in this region revealed a G-to-A mutation at position 371 in HR7 DNA that results in a Gly36-to-Glu substitution.
(C) The ech2-1 mutation disrupts a conserved Gly (asterisk). Sequences from predicted ECH2 homologs (accession numbers in [D]) and MFE2 homologs were aligned using the MegAlign program (DNAStar; full alignment and accession numbers are in Supplemental Figure 5 online).
(D) Phylogenetic tree of ECH2, IBR10, MFE2, MFP2, AIM1, and relatives. Protein portions corresponding to the hydratase domains were aligned using ClustalW (alignment in Supplemental Figure 6 online and Supplemental Data Set 1 online), and the unrooted phylogram was generated using PAUP 4.05b (Swofford, 2001) by performing the bootstrap method with 500 replicates. Bootstrap values are shown at the nodes.