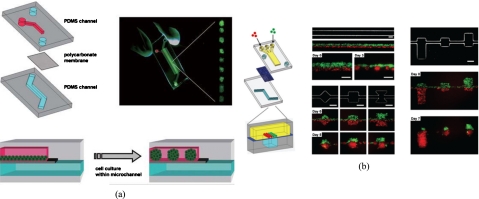
Figure 6.
(a) Schematic illustration of the microfluidic EB formation device. Two PDMS microchannels are separated by a semiporous polycarbonate membrane, and the cells self-aggregate and form EBs because channel surfaces are rendered resistant to cell adhesion. [Reprinted with permission from Y. S. Torisawa et al., Lab Chip 7, 770 (2007). © 2007, The Royal Society of Chemistry.] (b) Two types of cells, MDA-MB-231 cells (green) and COS7 cells (red), are juxtaposed in the top layer as fluid flow focuses them together into one channel in the bottom layer, and cellular patterning on the bottom channel with distinct geometric features for shape control. [Reprinted with permission from Y. S. Torisawa et al., Integr. Biol. 1, 649, (2009). © 2009, The Royal Society of Chemistry.]