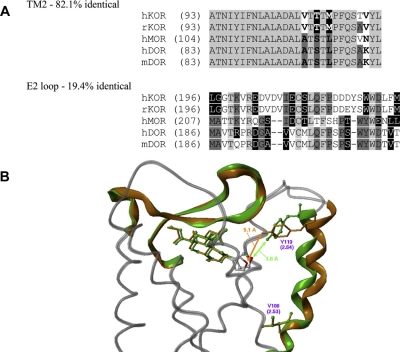
Fig. 11.
Graphical representations of the human KOP receptor. A, amino acid sequence alignments for TM II and the EL II of human and rat KOP receptor (hKOR and rKOR, respectively), human MOP receptor (hMOR), and human and mouse DOP receptor (hDOR and mDOR, respectively). B, molecular models of KOP receptor before rotation (green) and after rotation (orange) with salvinorin A docked and energy minimized in both receptors. [Reprinted from Vortherms TA, Mosier PD, Westkaemper RB, and Roth BL (2007) Differential helical orientations among related G protein-coupled receptors provide a novel mechanism for selectivity. Studies with salvinorin A and the kappa-opioid receptor. J Biol Chem 282:3146–3156. Copyright © 2007 The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Used with permission.]