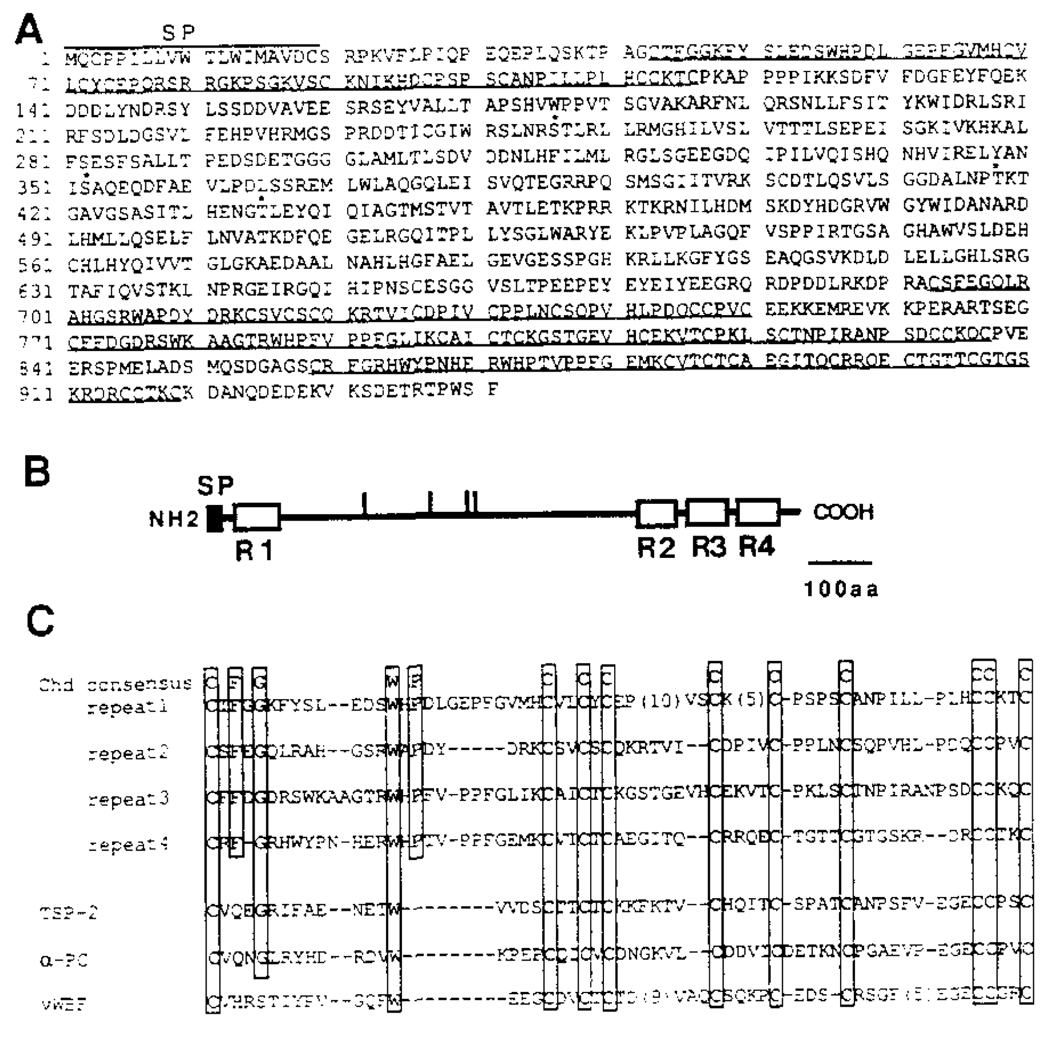
Figure 4. Xenopus chordin Encodes a Putative Secreted Protein.
(A) The amino acid sequence deduced from the nucleotide sequence of a full-length Xenopus chordin cDNA clone is shown. The initiator Met was assigned to the first ATG in the longest reading frame, which has an in-frame stop codon 130 bp upstream of this ATG. Four potential N-glycosylation consensus sequences are indicated by asterisks. Four internal repeats are underlined. A hydrophobic signal peptide segment is found at the amino terminus (residues 1–19).
(B) Schematic structure of chordin protein. The potential signal peptide and four internal Cys-rich repeats are shown by closed and open boxes, respectively. Vertical bars indicate potential N-glycosylation sites. SP, signal peptide.
(C) Comparison of Cys-rich repeats in chordin and those in some secreted proteins. The residues conserved among four repeats are boxed. chd, Xenopus chordin; TSP-2, mouse thombospondin-2; α-PC, human α1 procollagen type I; vWBF, human von Willebrand factor C1 domain.