Figure 3.
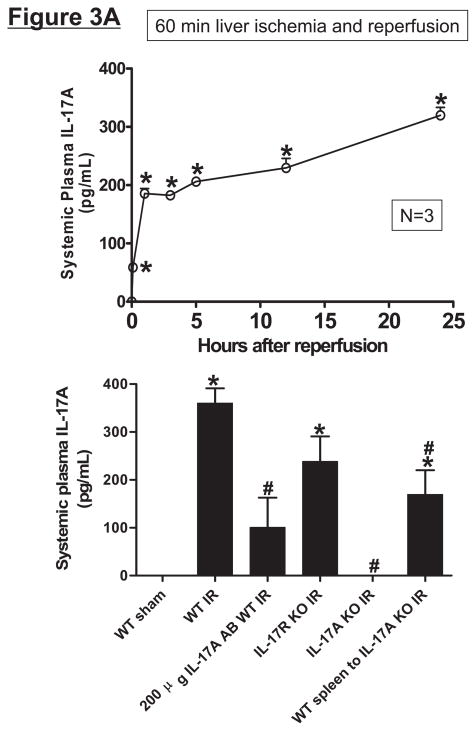
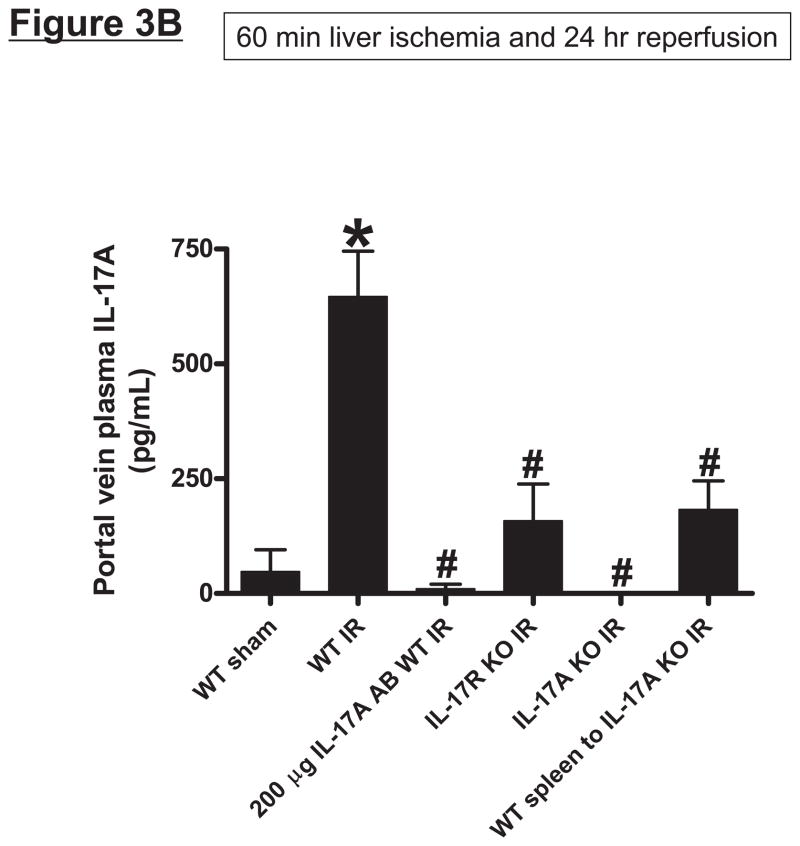
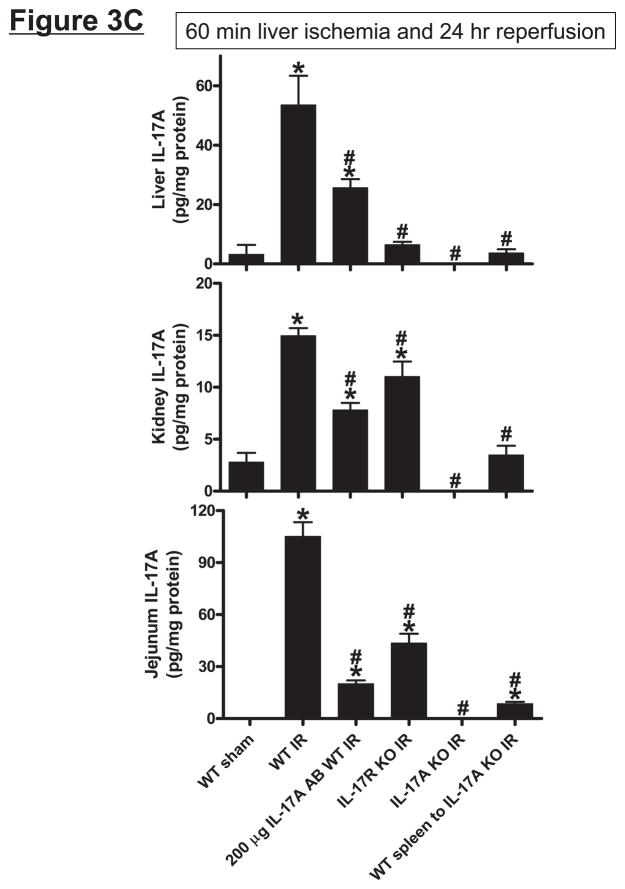
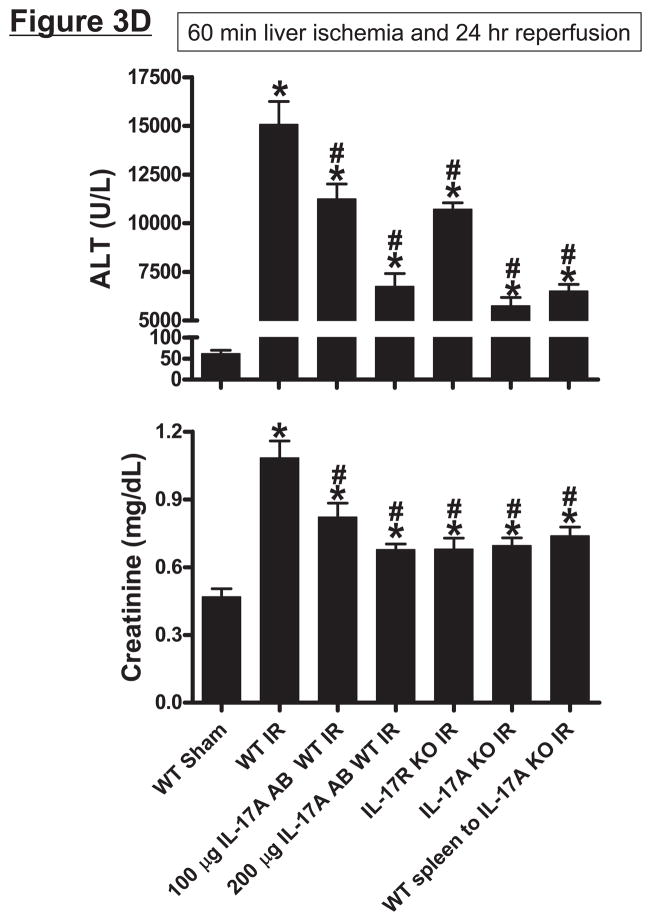
Systemic (A) and portal plasma IL-17A levels (B), liver, kidney and small intestine (jejunum) IL-17A levels (C) and indices of hepatic (ALT) and renal (creatinine) injury (D) from mice subjected to sham-operation (Sham, N=4) or 60 min. hepatic ischemia and reperfusion (IR, N=6). Sixty min. liver IR resulted in rapid increases in plasma IL-17A levels in mice (N=3, A). Neutralization of IL-17A (IL-17A AB, 100 or 200 μg iv, N=5 each), deficiency in IL-17A receptor (IL-17R KO, N=5) or IL-17A (IL-17A KO, N=5) reduced plasma and tissue IL-17A levels and protected against hepatic and renal injury 24 hr after 60 min. hepatic IR compared to WT mice. IL-17A deficient mice (N=5) transfused with wild type splenocytes (Wild type spleen to IL-17A KO) also had significantly lower plasma and tissue IL-17A levels and were also protected against liver and kidney injury 24 hr after 60 min. hepatic IR. *P<0.05 vs. sham-operated mice. #P<0.05 vs. WT mice subjected to hepatic IR. Error bars represent 1 SEM.