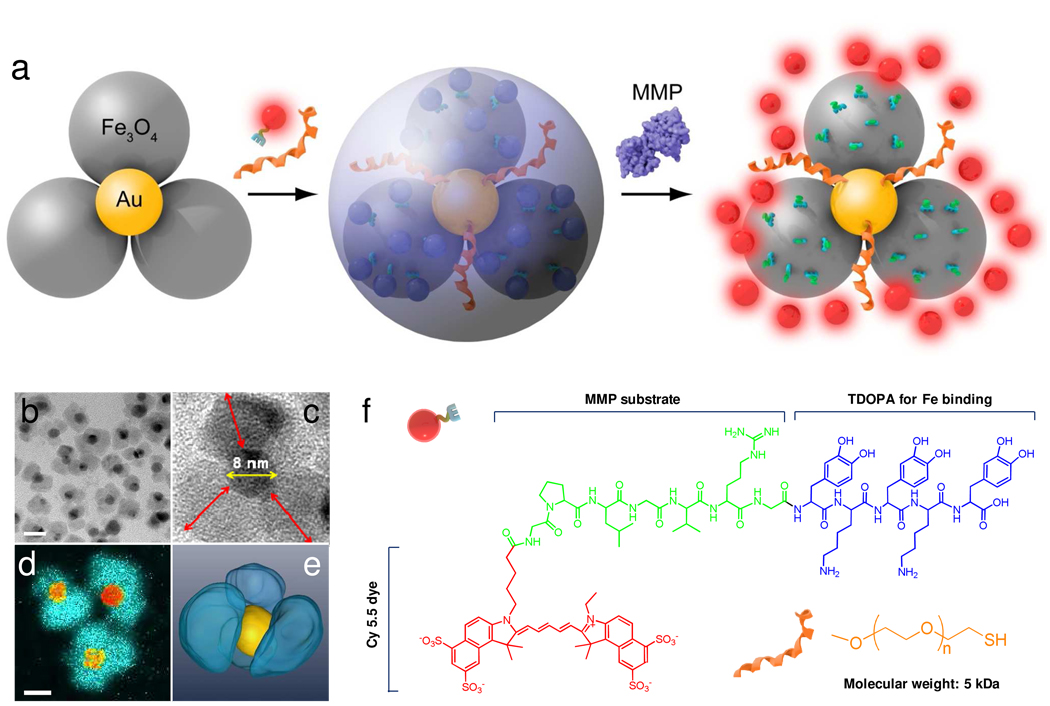
Figure 1.
a) Schematic illustration of the formation and working mechanism of FANPs. b) High resolution TEM of the flower-like Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Scale bar = 20 nm. c) Enlarged TEM image of a representative flower-like Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticle. The diameter of the GNP core is about 8 nm. The longest distance between the IONP surface and the GNP surface, labeled as red arrows, is 9.7 ± 1.4 nm. d) Iron map (blue green) super positioned with the gold cores (yellow orange) obtained with an electron microscope in the EFTEM mode. e) surface-rendered tomogram of a nanoparticle, where false coloring is based on the elemental mapping in d). f) Chemical structures of Cy5.5-GPLGVRG-TDOPA and SH-PEG5000.