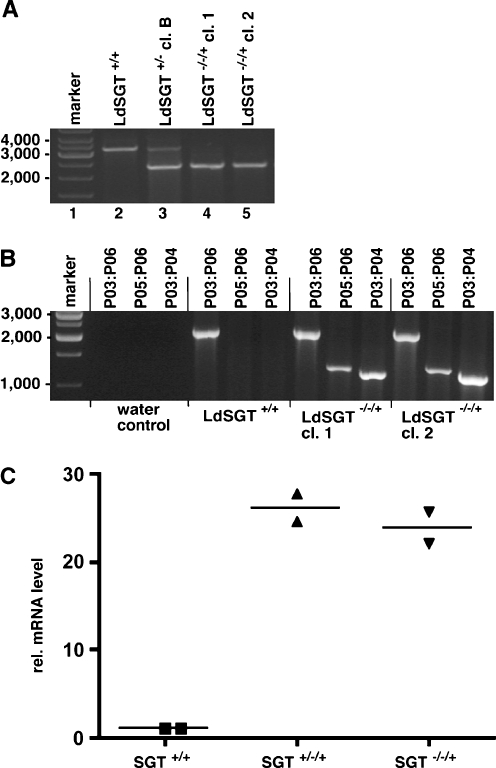
Fig. 4.
PCR analysis. a Verification of LdSGT gene replacement. Genomic DNA derived from wild-type L. donovani (LdSGT+/+), a single-allele replacement clone (LdSGT+/− clone B) and two putative LdSGT−/−/+ clones was used as template for PCR. Amplification of the SGT locus using primers P01 and P02 (Fig. 3). Primers anneal to sequences outside the region homologous to the gene-replacement constructs, yielding a predicted PCR product of 3,219 bp. Replacement of the SGT ORF with BleoR and PuroAC, respectively, results in PCR products of 2,368 and 2,591 bp. b Test for correct integration of the add back gene. Genomic DNA from LdSGT+/+ and two LdSGT−/−/+ clones was used as template for PCR. The primer pair P03:P04 or P05:P06 (Fig. 3), as indicated above the lanes, only allow the amplification of 1,156 and 1,247 bp products if the LdSGT add back construct are correctly integrated into an 18S rRNA gene unit. The combination of primer P03 and P06 was used as positive control. c Semiquantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of LdSGT mRNA. RNA isolated from wild-type L. donovani LdSGT+/+, from a SGT single-allele mutant with add back LdSGT+/−/+, and from a LdSGT−/−/+ clone was reversely transcribed. The resulting cDNAs were used for semiquantitative real-time PCR using specific primers for LdSGT. For normalization of the results, actin mRNA was amplified, too. The analysis was performed in duplicate from each sample; the horizontal bars mark the mean of two results. The Y-axis shows the relative mRNA levels calculated relative to the actin signal