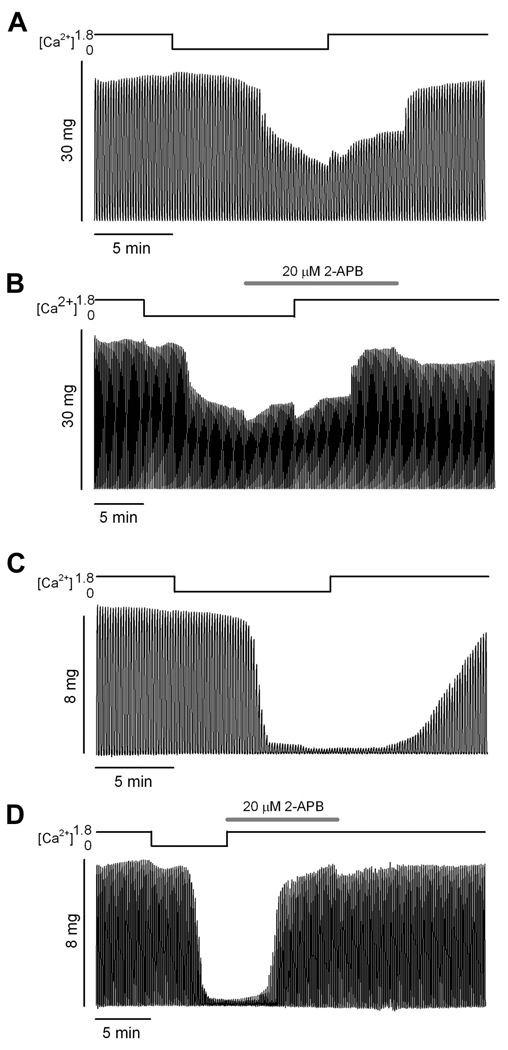
Figure 3. 2-APB action on tetanic force recovery.
A and B. Tetani from a single intact FDB fiber of an aged mouse recorded during two exposures to Ca2+-free solution. The traces in A illustrate a 0Ca trial (see Methods). The traces in B illustrate a 2-APB trial in which the 2-APB was introduced during 5 min of contraction in Ca2+-free solution prior to return to normal physiological solution (see Methods). Force decline was virtually identical in the two trials. Note that force recovery in the 2-APB trial occurred in the presence of 1.8 mM Ca2+ (physiological solution) and in the presence of 2-APB. C and D. Tetani from a single intact FDB fiber of an aged mouse recorded during two exposures to Ca2+-free solution. Traces in C illustrate a 0Ca trial (see Methods). Force decline in this experiment was greater than that illustrated in A and B. Force fully recovered to baseline within 5 min after the experiment (data not shown). Traces in D illustrate a 2-APB trial in which the 2-APB was introduced simultaneously with return to physiological solution. Force fully recovered in the presence of 2-APB. Note the variable onset of the decline in tetanus amplitude after incubating the muscle fiber in Ca2+ free medium. Traces are representative of 6 fibers from 6 mice.