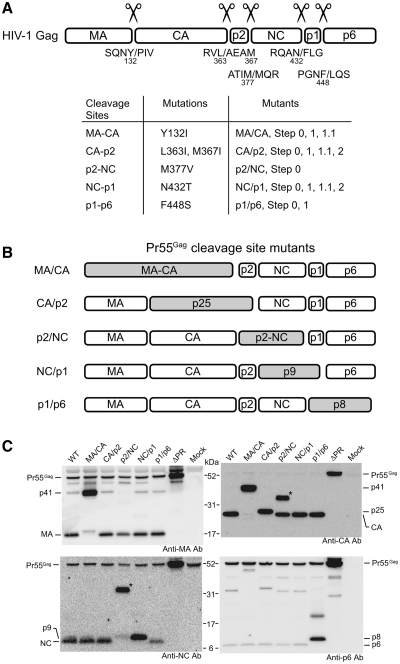
Figure 1.
Gag-cleavage site mutations of HIV-1. (A) Summary of the mutations used in this study. Upper figure represents HIV-1 Gag and its cleavage site sequences. The slashes represent the position of cleavage and the numbers beneath the letters designate amino acid positions in Pr55. The correlation between the mutation and the mutants constructed are summarized in the table. Details on the mutations Y132I, M377V, N432T and F448S have been reported (23), as well as the L363I and M367I mutations (16). The M367I mutation was introduced to block an HIV-1 PR-mediated cryptic cleavage site within the p2 protein because this cryptic cleavage has been reported to occur when proteolytic cleavage between CA and p2 was inhibited by L363I mutation. (B) Schematic representations of the single Gag-cleavage site mutants. Shaded boxes represent fusion proteins which resulted from the mutations. (C) Detection of HIV-1 protein produced in pelleted virions by western blotting with various anti-Gag antibodies. Positions of Gag proteins and precursors were indicated. The asterisks indicate aberrant proteins (‘Results’ section).