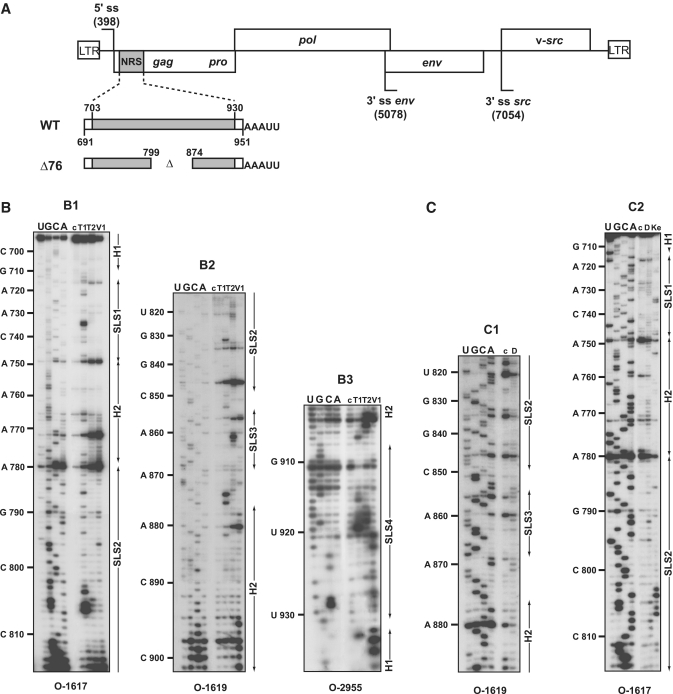
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the RSV Prague C (PrC) genome and of the NRS RNAs used for secondary structure analyses. The architecture of the RSV PrC genome is shown on top of the Figure. The 5′-ss and 3′-ss are indicated and boxes represent the open reading frames. The grey box depicts the NRS element (nucleotides 703–930) located in the gag gene used for secondary structure experiments. Viral sequences belonging to the RSV segments located upstream and downstream from NRSs are in white. The non-viral AAAUU sequence at the 3′-end of the transcripts is shown. Delimitations of NRS are indicated according to NRS nucleotide numbering (48). (B and C) Primer extension analyses of enzymatic cleavages and chemical modifications of NRS WT. (B) Primer extension analyses of enzymatic cleavages in NRS WT (position 691– 951) (B1–B3), (C) primer extension analyses of chemical modifications in NRS WT (position 710 to 890) (C1 and C2). T1, T2, V1, D and Ke above the lanes indicate T1, T2, V1 RNase digestions and DMS or Kethoxal modifications, respectively. Conditions for digestions, modifications and reverse transcription are given in ‘Materials and Methods’ section. Lanes c correspond to control experiments with untreated RNA; lanes U, G, C and A correspond to the sequencing ladder. Primers used for reverse transcription are indicated below each autoradiogram (see Supplementary Table S1 for their nucleotide sequences). Nucleotide numbering according to (48) is indicated on the left side of the autoradiograms. Positions of the stem–loop structures (SLS1, SLS2, SLS3 and SLS4) and the helices (H1 and H2) are shown on the right side of the autoradiograms.