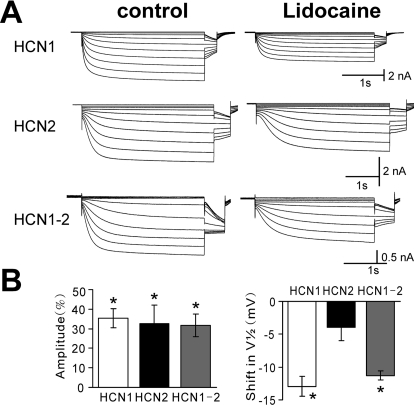
Fig. 1.
Local anesthetic lidocaine differentially inhibits HCN channel currents expressed in X. laevis oocytes. A, sample currents from X. laevis oocytes expressing mHCN1, mHCN2, and mHCN1-mHCN2 channel constructs evoked by hyperpolarizing voltage steps from −40 to −120 mV before and during exposure to lidocaine (100 μM); conditioning voltage steps were of different duration for the three constructs (3, 4, and 3 s) followed by a step to −90 mV for tail current analysis. B, summary data showing averaged (± S.E.M.) current inhibition (percentage from control; left) and shift in half-activation potential (V1/2; right) evoked by lidocaine for each of the indicated HCN channel constructs. *, P < 0.05 by analysis of variance for lidocaine versus control (n = 6, 5, and 8 for mHCN1, mHCN2, and mHCN1-mHCN2, respectively).