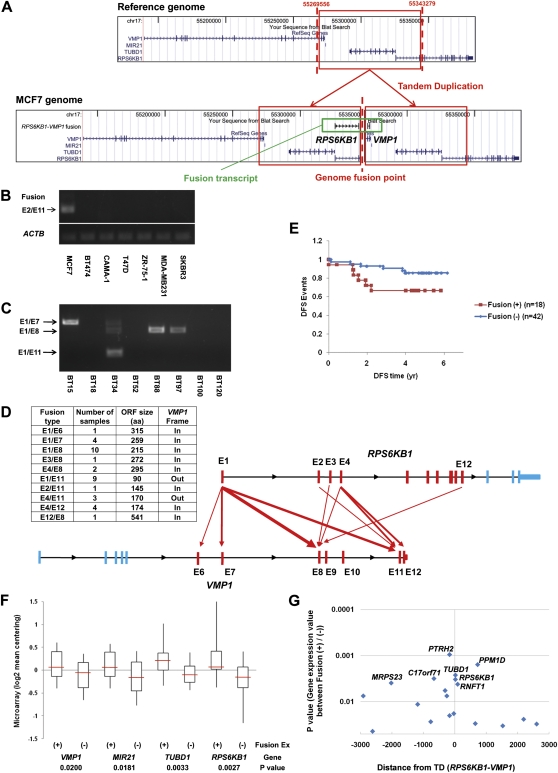
Figure 4.
Expression of recurrent fusion gene transcript (RPS6KB1-VMP1) in breast cancer. (A) Structure of the fusion gene transcript created by a tandem duplication (TD) in the 17q23 locus in the MCF-7 genome. The genome DNA rearrangement point detected by DNA-PET data was validated by genomic PCR and sequencing. Expression of the fusion transcript in breast cancer cell lines (B) and in primary tumor samples (C) determined by RT-PCR. (D) Fusion pattern of the transcripts in primary tumor samples showing a range of exons included in the fusions. (E) Correlation of the fusion expression and disease-free survival (DFS) in breast cancer patients. Sixty patients with available information were separated into two groups (18 fusion [+] and 42 fusion [−]) and disease-free survival events were analyzed. Expression of the fusion showed a trend toward correlation (P = 0.06) with poor prognosis of the patients. Correlation of the expression of the fusion with those of genes involved in the TD (F) and with those of neighboring genes (G) within a 3-Mb window from the TD in breast cancer primary tumors. Sixty-eight patient samples with available information were separated into 21 fusion (+) and 47 fusion (−), and the expression of the genes were compared. P-values (<0.05) for the difference of each gene expression between the fusion (+) and (−) samples are shown on each gene location. PTRH2 (P = 0.0010), PPM1D (P = 0.0016), C17orf71 (P = 0.0031), MRPS23 (P = 0.0039), and RNFT1 (P = 0.0042) showed significant correlation as well as TUBD1 and RPS6KB1.