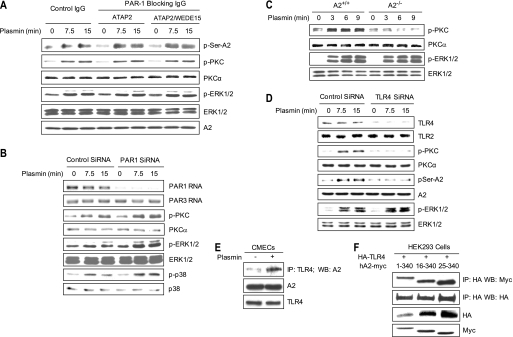
FIGURE 6.
Plasmin-induced PKC activation is mediated by A2 and TLR4 but not PAR1. A, HUVECs were preincubated with either isotype control IgG, the PAR-blocking antibody ATAP2 (20 μg/m), or ATAP2 (10 μg/ml) plus a second PAR-blocking antibody, WEDE15 (25 μg/ml), for 30 min and then stimulated with plasmin (0.3 unit/ml; 7.5 or 15 min). Serine phosphorylation of A2 was assessed by coimmunoprecipitation. Total levels of phospho-ERK1/2, -PKC, and -A2 were analyzed by immunoblotting. B, HUVECs were transfected with Accell siRNA directed against human PAR1, treated as indicated, and blotted with anti-phospho-PKC, -PKCα, -phospho-ERK1/2, -ERK1/2, -phospho-p38, and -p38. Steady state levels of PAR1 and PAR3 mRNA, as detected by RT-PCR, are shown in the first two panels. C, primary A2+/+ and A2−/− CMECs were treated with plasmin for 3, 6, or 9 min, after which phospho-PKC and -ERK1/2 were compared. D, HUVECs were transfected with Accell siRNA for human TLR4, treated as indicated. The levels of phospho-PKC, phospho-ERK1/2, serine phosphorylation of A2, and A2 were measured by immunoblotting. Specificity of the knockdown was shown by immunoblot analysis of TLR4 and TLR2 protein. E, membrane fractions were isolated from plasmin-treated CMECs and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-mouse-TLR4 IgG, and the precipitates were immunoblotted with anti-A2 IgG. Total cell lysates were also blotted with anti-A2 and anti-TLR4 antibody. F, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding HA-tagged TLR4 and either full-length (residues 1–340) or two N-terminal deletion versions of Myc-tagged A2 (residues 16–340 and 25–340). Two days later, total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA and then blotted with anti-Myc or anti-HA IgG. Total expression of HA-TLR4 and Myc-A2 mutants was assessed by immunoblot analysis.