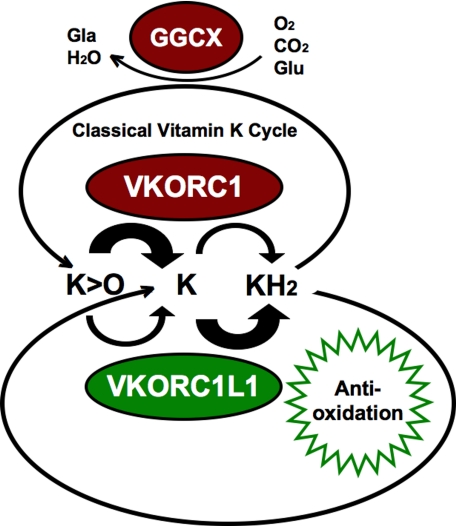
FIGURE 5.
A proposed grand vitamin K cycle. Shown are proposed functional relationships among vertebrate VKORC1L1 and VKORC1 paralog enzymes, GGCX responsible for post-translational protein γ-glutamyl carboxylation, and reducing equivalent exchange functions of K vitamins in the ER membrane. Glu, glutamyl protein residue; Gla, γ-carboxylated glutamyl protein residue; K, vitamin K quinone. Enzymes depicted as ovals: GGCX, γ-glutamyl carboxylase; VKORC1, red ovals represent enzymes of the “classical” vitamin K cycle; VKORC1L1, green oval. Thick arrows indicate relative turnover rates of naphthoquinone substrates K > O and vitamin K quinone by VKORC1L1 (lower pair of arched arrows) and by VKORC1 (upper pair of arched arrows). Antioxidative function of KH2 is depicted as a green sunburst.