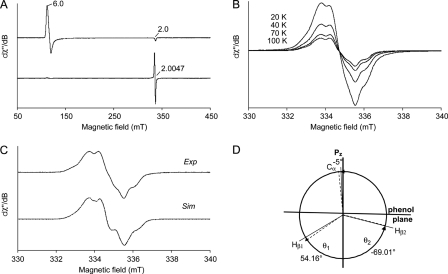
FIGURE 6.
Low temperature EPR spectra of T.cervina LiP*. A, spectra of LiP* resting state (top) indicating the high-spin ferric signals (g = 2.0 and 6.0), and its peroxide-activated form (Compound I) (bottom). B, effect of temperature (20, 40, 70, and 100 K) on the EPR signal in the peroxide-activated LiP*. C, high-resolution narrow scan spectrum of the protein radical in the peroxide-activated LiP* (Exp) paired with its simulation (Sim). D, schematic representation of the dihedral angles θ1(Hβ1), θ2(Hβ2), and θ3(Cα) of Tyr-181 in the LiP* crystal structure (dashed lines), together with those calculated from the EPR data (solid lines). EPR spectra were recorded under the following conditions: ν, 9.4 GHz; modulation amplitude, 1 (A) and 0.1 mT (B and C); microwave power, 2 (A) and 0.2 milliwatts (B and C); modulation frequency, 100 kHz; and temperature 4 (A) and 100 K (C).