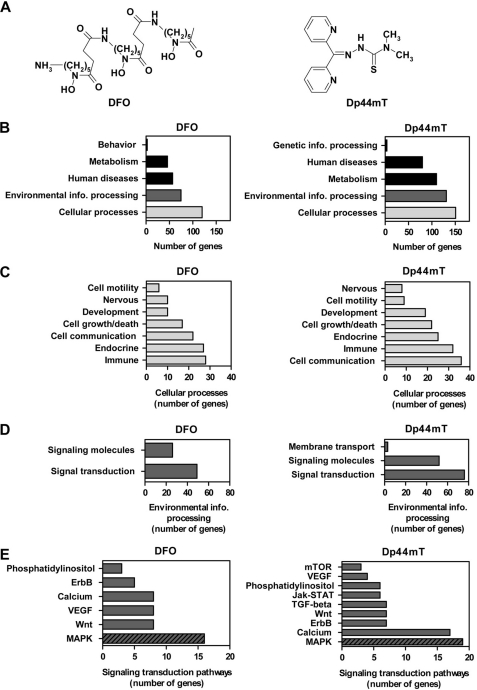
FIGURE 1.
Structures of the chelators used and microarray data showing that DFO and Dp44mT significantly alter the expression of a large number of genes involved in the MAPK signaling transduction pathway. A, chemical structures of DFO and Dp44mT. B, functional pathway annotation of genes significantly altered (p < 0.05) by DFO (250 μm) or Dp44mT (25 μm) after a 24 h/37 °C incubation of DMS-53 lung cancer cells as assessed by a human genome gene array (Affymetrix U133 plus 2.0 array). Only genes with a greater than log2 value of 1.0 as compared with the control were included in the analysis. Genes in the category of cellular processes (C) and environmental information processing (D) were further sub-categorized according to their functions. E, various signaling transduction pathways affected. Lists of genes were assessed using DAVID. Pathway annotation was obtained through the public data base, KEGG pathway mapping.